Setting smart objectives
- 1. Setting Smart Objectives Prepared and Presented By: Dr. Yaser Aref CEO, MGP Management Consultancies
- 2. SMART Objectives Job Aid Use the SMT+AR Table What result will you deliver? How will you know you did good work? When will you deliver your result? How will your result add value? On what will your success depend? Write no more than one bullet Write at least one bullet, best not to exceed five Write at least one bullet, more are possible Must ask the question, may or may not write the answer Must ask the question, may or may not write the answer prefer noun and adjective focus on what lies ahead apply multiple measures list conditions for success link to organizational goal S M A R T
- 3. SMART Objectives Job Aid Job Objective Pointers Don’t describe your work, drive your work. It’s about the future, not the past. Focus on what lies ahead and what you will contribute. Think noun and adjective. Use nouns and adjectives to name the result. Save verbs and adverbs for your action plan. Build multiple measures into every objective. Multiple measures increase the likelihood of your success and the quality of your product. Identify the right measures to get the right result. Ask yourself, “How will I know I did good work?” Good work is the right result, however it is defined. Target Level 3 performance. Be clear about what your organization needs you to accomplish, then make it happen. Focus on what matters most. Every contribution you make matters, though not all your contributions will be rated.
- 4. Results Performance Management Means Evolution “change management” • Not just short term boost • Continuous behavioral change • Long term business success
- 5. Business ? • No longer easy to do business • LARGE competition. • Bad international financial climate • Business Improvement Discussions – Identify known needs from managers – Identify unknown needs from analysis within organization
- 6. 6 Introduction Of all the functions involved in management, planning is the most important. As the old saying goes, “Failing to plan is planning to fail”. Setting goals and objectives is the first and most critical step in the planning process. Employers need to be sure all employees are well trained in how to set these important performance measurements. This sample presentation is intended for presentation to all employees. It is designed to be presented by an individual who has knowledge of the basics of setting goals and objectives, of the employer’s own policies and practices on goals and objectives setting, tactical and strategic planning, and performance management. This is a sample presentation that must be customized to include and match the employer’s own policies and practices.
- 7. 7 Goals vs. Objectives Goals • General • Intangible • Broad • Abstract • Strategic – long-range direction, set by top executives Objectives • Specific • Measurable • Narrow • Concrete • Tactical – short-range, set by mangers to accomplish goals Although the terms “goals” and “objectives” are often used interchangeably, there is a difference between them:
- 8. 8 Quiz – Goals vs. Objectives Which of these are goals and which are objectives? 1. Increase profitability 2. Improve community relations 3. Provide short-term disability insurance to employees by mid-year 4. Improve employee computer skills *Note to presenter: Ask “Is this a goal or an objective?” If a goal, ask what the related objective would be – if an objective, ask what the general goal might be
- 9. 9 Importance of Setting Goals & Objectives • Planning is the most important management function. – As the old quote goes, “Failing to plan is planning to fail” • Setting goals and objectives is important because it is the first and most critical step in a company’s planning process.
- 10. 10 How We Set Goals & Objectives • At (name of company) top management establishes our corporate goals each year and for the next 3-5 years as part of the company’s strategic plan. • Under our Management by Objectives (MBO) process, individual managers use these goals to set their departmental objectives, their own objectives, and their employee’s individual objectives. • We evaluate quality of performance of managers and employees based primarily on their accomplishment of these objectives.
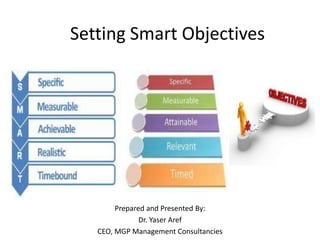
- 11. 11 SMART Objectives At (name of company) we set SMART Objectives: S Specific M Measurable A Achievable R Realistic T Time-oriented
- 12. 12 Specific Objectives Specific objectives are: • Concrete • Detailed • Focused • Well-defined • Straight-forward • Action-oriented
- 13. 13 Specific Objectives cont’d. When setting objectives that are specific, ask: • What am I going to do? Use action verbs such as develop, execute, conduct, build • Why is it important to do this? • Who is going to be involved? • When do I want this to be completed? • How am I going to do this?
- 14. 14 Measurable Objectives • Measurements for objectives help you know when you have accomplished them. • If you set an objective that is measurable, when you complete it you have tangible evidence of completion.
- 15. 15 Measurable Objectives cont’d. When setting objectives that are measurable, ask: • How will I know when this objective has been achieved? • What measurements can I use?
- 16. 16 Achievable Objectives • Achievable objectives are those that you can actually accomplish (something you can really do within the time frame set) and not an aspiration or vision. • Achievable objectives need to challenge you but not so much so as to be unattainable or to cause frustration in being unable to complete.
- 17. 17 Realistic Objectives Realistic objectives are those that you have the resources to accomplish including: – Skills – Funding – Equipment – Staff
- 18. 18 Realistic Objectives cont’d. When setting objectives that are realistic, ask: – Do I have the resources to accomplish? – Do I need to rearrange my priorities to accomplish? – Is it possible to complete this objective?
- 19. 19 Time-Oriented Objectives • Time-oriented objectives are those which have deadlines for completion. The time frames create sufficient urgency and lead to action. • The deadlines, just as with overall objectives, must be achievable and realistic. • For a complex objective, break into small parts with a date for completion for each.
- 20. 20 When setting objectives that are time- oriented, ask: – What is the earliest yet achievable and realistic date for this objective to be completed? – Have I included this date in the statement of the objective? Time-Oriented Objectives cont’d.
- 21. 21 Course Evaluation Please be sure to complete and leave the evaluation sheet you received with your handouts. Thank you for your attention and interest!
- 22. Foundation of Learning Share your experiences. They provide valuable insight. If you are doing something that gets the results you want, keep doing it. Take the information you learn here and put it into your own style.
- 23. Goals and Objectives • Setting SMART Objectives (An Overview) • Getting SMARTer • Not only being SMART, but remembering what is Important • SMART –The way you need it explained • Getting Your Objectives Accomplished = Goal > Objectives > Strategies > Tactics • Measurements and ROI • Working backwards to get ahead
- 24. Polling Question #1 I know the difference between a goal and objective (It’s ok if you’re not sure) Yes No
- 25. Goals and Objectives Defined • Goals relate to our aspirations, purpose and vision. For example, I have a goal of becoming financially independent. • Objectives are the battle plan, the stepping stones on the path towards the achievement of my goal.
- 26. Getting SMARTer • Process objectives – Lets you know what you are doing and how you will do it; describes participants, interactions and activities • Impact objectives – Lets you know what the long term implications of your program/activity will be; describes the longer term impact on your target audience or organization
- 27. Getting SMARTer Outcome objectives Lets you know how you will change attitudes, knowledge or behavior (short term); describe the degree to which you expect this change Personal objectives Personal development is an ideal application for SMARTer objectives. Often we see SMARTer objectives written for project management or business and performance management, however as individuals in our personal development plans, SMARTer objectives are also a valuable formula within which to set and individual measure performance.
- 28. Key Components of a Work Objective Conditions Sets the situation and/or environment in which the staff member is required to work within... Acceptable levels of Performance Consider what level of performance is deemed acceptable in terms of Quality (i.e. how effectively the work should be performed), Quantity (i.e. how much is produced) and/or Timeliness (i.e. how quickly or in what timeframe the outcome is to be achieved). Measures Include clear measures (quality, quantity, cost, timeliness and frequency of completion) so both parties can track progress and readjust priorities if necessary, to ensure performance outcomes can be achieved
- 29. Polling Question #2 I have used the SMART model of setting either goals or objectives before in my work or personal life Yes No
- 30. SMART
- 31. Examples of SMART Objectives 1. Relationship Objectives To host quarterly FOL activities to build membership by 10%. (20 new members) 2. User Ship Objectives To increase the circulation of our DVD collection by 5% in the next 3 months. 3. Promotional Objectives To increase awareness of the library’s Adult Programming by adding banners to the library’s website and front entrance for 6 consecutive months beginning in January.
- 32. Examples of SMART Objectives 4. Objectives for Survival To survive the current economic recession. 5. Objectives for Growth To increase the size of our audio book collection by 3% in 2011. To increase the number of public use computers by 50% in fiscal year 2011-2012. 6. Objectives for Branding To make our library the preferred library of Young Adult Readers in Pinellas County by 2013.
- 33. Tests for a Good Objective—A Memory Tool • It must be Specific, • It must be Measurable, • It must be Attainable, There need to be enough Resources • It must be Timed, and • It must be IMPORTANT
- 34. How Do You Know What’s “Important”?
- 35. Time Frame
- 36. SMART objective are the stepping stones towards the achievement of our goals……
- 37. Specific • WHAT am I going to do? This are best written using strong, action verbs such as conduct, develop, build, plan, execute, etc. This helps your objective to be action-orientated and focuses on what’s most important. • WHY is this important for me to do? • WHO is going to do what? Who else need to be involved? • WHEN do I want this to be completed? • HOW am I going to do this?
- 38. Specific Diagnostic Questions • What exactly are we going to do, with or for whom? • What strategies will be used? • Is the objective well understood? • Is it clear who is involved? • Is it clear where this will happen? • Is it clear what needs to happen? • Is the outcome clear? • Will this objective lead to the desired results?
- 39. Measured If the objective is measurable, it means that the measurement source is identified and we are able to track the results of our actions, as we progress towards achieving the objective. Measurement is the standard used for comparison.
- 40. Diagnostic Questions • Can we get it done in the proposed timeframe? • Do I understand the limitations and constraints? • Can we do this with the resources we have? • Has anyone else done this successfully? • Is this possible?
- 41. Realistic Objectives that are achievable, may not be realistic….. however, realistic does not mean easy. Realistic means that you have the resources to get it done. The achievement of an objective requires
- 42. Time Bound Time-bound is defined as setting deadlines for the achievement of the objective. Deadlines create an important sense of urgency. If you don’t set a deadline, you will reduce the motivation and urgency required to execute the tasks. Deadlines create the necessary urgency and prompts action.
- 43. Goals vs. Objectives • Goals are your general intentions, the big picture aims. Your objectives are the outcomes that represent achievement of that goal. Things you can actually observe. In order to be classified as an objective, something has to be measurable. You need a way of defining whether or not you have completed them successfully
- 44. Measurement and ROI Measuring success, however, can be different than ROI. You can have successful outcomes that are not measurable in terms of dollars. Qualitative ones like awareness and reach, and quantitative ones like website traffic.
- 45. Working Backwards From Your Goal to Get Ahead
- 46. Thanks for Attending Our Next Program with PCI Webinars! Performance Gap Analysis in Your Library with Ned Parks Wednesday, December 15th at 1:00 pm
- 47. Demand the best from yourself, because others will demand the best of you. . . . Successful people do not simply give a project hard work. They give it their best work.” Win Borden
- 48. Becoming An Agility Master • Great leaders have learned the art and science of mastering self-improvement and time management • In many ways, these principles apply to salespeople • To be effective in sales, one must have courage and a positive attitude, even in the face of adversity
- 49. Six Aspects of Leadership • Each aspect can be applied to selling and to life in general 1. Having a set of beliefs and sticking with them 2. Optimism 3. Courage 4. Relentless preparation 5. Teamwork 6. Communication Mayor Rudy Giulianni, from a speech given to the Direct Selling Association on June 11, 2003
- 50. Self-Discipline • Learning to manage oneself and one’s time requires self-discipline, which requires determination • Determination begins with a purpose or a “calling,” the creation of passion, which drives one toward reaching specific goals
- 51. “Your dreams will not progress to failure unless you fail to progress” Fern Jones
- 52. Becoming Self-Disciplined • Self-discipline is defined as making a “disciple” of one’s self – Becoming one’s own teacher, trainer, coach, disciplinarian • Becoming disciplined helps salespeople develop and manage their personal and professional goals (their purpose) Source: William J. Bennet, The Book of Virtues
- 53. Habits: Powerful Factors • A good habit, consisting of three elements, is defined as “the intersection of knowledge” 1. Knowledge: the what to do 2. Skill: the how to do 3. Desire (motivation): the want to do Source: Stephen Covey, The Seven Habits of Highly Effective People
- 54. Seven Habits of Highly Effective People • Stephen Covey’s seven habits are: – Be proactive – Begin with the end in mind – Put first things first – Think win/win – Seek first to understand and then to be understood – Synergize –Sharpen the saw Refer to Table 13.1--How the Seven Habits Apply to Salespeople
- 55. Sharpen the Saw Effectiveness and Efficiency • Successful people are accountable for how they manage both themselves and their time – Managing oneself is largely concerned with learning how to make oneself more effective – Managing time is largely concerned with making oneself more efficient
- 56. “Always demanding the best of oneself, living with honor, devoting one’s talents and gifts to the benefit of others— these are the measures of success that endure when material things have passed away” Gerald Ford
- 57. Managing Oneself • When people engage in self-management, they are engaging in a practice of determining what qualities lead to agility and success • Self-management also involves learning how to develop those qualities to build and maintain relationships
- 58. Success In Today’s Knowledge Economy • Success in today’s knowledge economy comes to those who know: – Their strengths – Their values – How they best perform
- 59. Accountability • Why some people succeed and others do not is largely due to how they manage their accountabilities • Accountability refers to being responsible for someone or some activity – Two facets 1. Simply performing the activities specified 2. How effectively the person performs those activities
- 60. Maintaining Accountability • Maintaining accountability involves several aspects: – What the salesperson wants to be – How the salesperson is going to get there – The salesperson’s assessment of how she is doing
- 61. “A great attitude does much more than turn on the lights in our worlds; it seems to magically connect us to all sorts of serendipitous opportunities that were somehow absent before we changed” Earl Nightingale
- 62. Attitude: The Great Motivator • The difference between the professional and the amateur is more a matter of attitude • Having the agility to compete successfully depends on many things, but high on the list is attitude • Attitude conveys a zeal for the work and a sincerity of interest in it
- 63. Image • A professional image is extremely important • Image is a function of both physical qualities and personal qualities • A person’s image is a mental picture of what others think of that person • Remember, a person never gets a second chance to make a first impression Review Chapter 7--Attention
- 64. Physical Qualities • Physical qualities are those that a customer can see or hear • The physical dimension of “sharpen the saw” is caring for our bodies – Eating the right foods – Exercising – Getting enough rest and relaxation
- 65. “Success Breeds Success” People who look successful will be perceived as successful
- 66. Personal Qualities of Agile Salespeople • Ego Drive • Empathy • Commitment • Maturity • Personal Magnetism • Sincerity • Self-Confidence • Trainability Refer to Table 13.3--Qualities of Successful Salespeople
- 67. Ego Drive • Ego Drive is a balance within oneself –Energy: • Some goal must energize the salesperson –Image: • The salesperson must have a good self image –Optimism: • The salesperson must remain optimistic about achieving her goal
- 68. Empathy • Throughout Selling ASAP, the importance of having empathy has been emphasized • Empathy is the capacity to participate in another person’s feelings or ideas • Agile salespeople can put themselves in their customers’ situations • Only with empathy can salespeople truly understand customers and inspire them
- 69. Commitment • The spiritual dimension of “sharpening the saw” has to do with commitment to one’s value system • A person’s value system inspires that person and affects how he treats other people – In a sales context, commitment encompasses the feelings a salesperson has toward the various aspects of his sales career and his customers
- 70. Maturity • A mature person is one who can make personal adjustments to people and circumstances • Salespeople show maturity in their ability to control personal feelings • Self-control is a necessary attribute of the successful salesperson Review the Social Styles Matrix in Chapter 5
- 71. Personal Magnetism • Personal magnetism is a combination of enthusiasm, intelligence, and smartness • It is a trait that strongly attracts others to those who have it • Salespeople who have personal magnetism are just that much more ahead of their competition
- 72. “Sincerity and truth are the basis of every virtue” Confucius
- 73. Sincerity • A mental dimension of “sharpening the saw" is sincerity • Sincere salespeople develop trusting relationships with customers – Sincerity convinces the prospect that the salesperson knows what she is talking about – Sincere salespeople are truly convinced that their products and services will meet their customers’ needs and wants
- 74. Self-Confidence • Self-confidence is – The belief in oneself or one’s own abilities – The belief that success comes from hard work and intelligent effort, not luck • Covey’s first habit, be proactive, means that salespeople must take responsibility for what they do – Taking initiative requires self-confidence Refer to Table 13.2--How Salespeople Can Develop Self-Confidence
- 75. Trainability • Successful people respond well to training and view learning as an opportunity for improving themselves • Achievers are those who thrive on new data and welcome a new challenge
- 76. Complacency • Complacency is feeling secure and ignoring any threats that exist • Complacency can erode salespeople’s relationships with their customers • Salespeople who become complacent risk using obsolete sales tactics Refer to Table 13.4 Things Salespeople Should Avoid
- 77. Managing Time • Covey’s third principle deals with prioritizing • The primary reason people cannot find time to be reflective is that they mix up what is urgent and what is important
- 78. “People become addicted to the urgent. They simply define important as urgent. They neglect preventive thinking, they neglect long-term strategic thinking, they neglect the building of high trust relationships, and they are consumed by an addiction called urgency” Stephen Covey
- 79. Importance and Urgency • Four combinations of importance and urgency relate to activities in which salespeople engage: – Not important, not urgent – Not important, but urgent – Important, but not urgent – Important and urgent
- 80. How Much Is Time Worth? If annual earnings are . . . Every hour is worth approximately . . . $25,000 $13 $30,000 $15 $35,000 $18 $50,000 $26 $75,000 $38 $100,000 $50 $200,000 $102
- 81. It’s About Time • Time is a precious resource that should be used wisely • The allocation of time between nonselling and selling activities represents one of the salesperson’s most important challenges • The key for salespeople in building long-term relationships is to make sure that nonselling time has a focus
- 82. Success Is a Race Against Time • Advanced technology has accelerated the pace of work life • Time is part of the agile professional’s inventory • Agile sales professionals adjust their work habits to meet the changing demands on their time
- 83. The work you do between 8:00 A.M. and 5:00 P.M. is what you get paid to do The work you do between 5:00 P.M. and 8:00 P.M. is what gets you promoted
- 84. Professional Selling Efficiency • Efficiency is often described in the sales profession in the form of advice: “Plan your work, and work your plan” • The time-management challenge for salespeople is to separate the unnecessary from the essential • Salespeople must learn to assign priorities to important activities
- 85. Planning • Planning involves setting SMART objectives –Specific –Measurable –Attainable –Realistic –Time-based
- 86. Cycles of Productivity • Productivity involves making the clock work to a person’s advantage • Individuals must determine their own peak periods and use them to their advantage • Salespeople should do the most demanding activities when they are at their best
- 87. Suggestions for Managing Time • Set goals • Manage interruptions • Clear the clutter • Use multiple contact media • Learn to say no • Manage appointments • Call on prospects who can buy now • Put a time value on entertainment and travel • Increase personal efficiency
- 88. Setting Goals • By setting goals, people know exactly what is to be accomplished and where they want to be • In order to be effective goals must: 1. Be in writing 2. Be specific and relate to results 3. Be realistic 4. Have a time schedule and a target date for finishing each step as well as each goal Refer to Table 13.5--Possible Goals for the Salesperson
- 89. Managing Interruptions • Constant day-to-day interruptions are huge time-wasters for people – Unnecessary visits – Unplanned social conversations and meetings • Self-sabotage is another form of wasting time – Procrastination – Perfectionism
- 90. Clearing the Clutter • A good way for salespeople to eliminate clutter and get organized is to – Standardize all routine tasks – Consolidate tasks by combining separate but similar ones – Redistribute work to the appropriate people – Anticipate what is to come by identifying tasks that can be done in advance
- 91. Managing Appointments • Salespeople should work cold calls and appointments concurrently because this maximizes the salesperson’s available time • Many salespeople use both appointments and cold calls, reserving their cold calls for fact gathering and finding out about a company’s products Refer to Table 13.6 Working Appointments and Cold Calls
- 92. Calling on Prospects Who Can Buy Now • The salesperson’s best opportunity to impress prospects is on the first call • The average cost of a sales call is increasing • Calling on customers who are not “real” prospects costs a lot of money
- 93. Personal Efficiency • Salespeople who are striving to increase their efficiency should record their transactions using: – A Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) – A Pocket Calendar or Day Planner – A Tickler File
- 94. Those who are persistent and who work hard and work smart can fulfill their visions
- 95. Going Back In Time • The following are people who believed in themselves in spite of criticism from others – Michelangelo – The Wright Brothers – Benjamin Franklin – Henry Ford Can you name a few?
- 96. Stepping Out on Faith • History provides many accounts of individuals who stepped out on faith with an idea—with a dream • Their belief system, along with determination and perseverance, allowed them to run with purpose, in spite of criticism from the masses
- 97. PerseverePersist Pursue your dreams with courage and optimism The Authors of Selling ASAP Eli Jones, Carl Stevens & Larry Chonko Believe
- 98. College of Micronesia - FSM Planning & resources committee September 23, 2009 Performance Budget 98
- 99. Performance budgeting - guiding principles • Be focused on outcomes • Provide simple, accessible information • Be understood and used by all • Be flexible and responsive to the customer • Support interdepartmental efforts • Measure achievement • Encourage continuous improvement • Assist with strategic planning and demand management 99
- 100. Performance budgeting - what it does States desired core outcome to be achieved Measures the success in achieving results Helps focus on the high-level outcomes desired Makes the budget more understandable and relevant to the community Empowers staff with flexibility Shows success more comprehensively and clearly (Measures overall service effectiveness) Better alignment: • organizational structure, processes, customer- driven, performance appraisal, training 100
- 101. Performance based budgeting and management • Links $$ with results • Focuses government on key priorities • Provides legislature with more information to set budget • Enables holding departments accountable • Provides monitoring and reporting framework • Provides managers information necessary to improve 101
- 103. What are outcomes? •They define the purpose of a service •Why are we here? •What results can we expect from our efforts? •Programs are created around outcomes •Only core outcomes are measured 103
- 104. Program outcomes statements WHY? (outcome) A statement of the ultimate goal HOW? (services) A statement of the broad service areas HOW WELL? (measures) Specific measurements of success Four standard measures: Customer Satisfaction, Cost Efficiency, Budget/Cost Ratio, Individual Measures 104
- 105. Measures How Well? Measurement of the Success in Achieving the Core Outcome(s). Only high level measures should be used. The outcome measures should focus on quality, effectiveness and efficiency. What results you need to determine whether the purpose has been met. What performance targets (service standards) should be set? Is there at least one measure for each “by” or “through” (strategies) statement? 105
- 106. Measures Be based on program goals or objectives that tie to a statement of program mission or purpose Measure program results or accomplishments Provide for comparisons over time Measure efficiency and effectiveness Be reliable, verifiable and understandable Be reported internally and externally Be monitored and used in decision-making 106
- 107. Accreditation issues • Linking – Planning – Assessment (including program review) – Resource allocation • Commitment to continuous improvement • Culture of evidence – No “trust me” – Data is presented to support statements – Assumptions are recognized as assumptions and tests are made to determine there validity 107
- 108. What is in place at COM-FSM? Strategic plan (planning) Sets mission, values and priority goals of the college Continuous improvement cycle Balanced scorecard – key results by strategic goal (measures) Improvement plans (IAP worksheet #1) Links to institutional mission and goals (links to institutional outcomes to be included in revision) Links to program mission and goals What is to be accomplished (results) Strategies by which it will be accomplished Criteria for success established Linked to revised performance evaluation for supervisors 108
- 109. What is in place at COM-FSM? IAP Assessment Process • Assessment plans (IAP worksheet #2) – Links to intuitional mission and goals – Links to program mission and goals – Evaluation questions for each improvement outcome/objective – Criteria by which you determine success – Data sources, sampling analysis identified – Timelines and who is responsible • Assessment reports (IAP worksheet #3) – Were the Improvement outcomes/results achieved to the specified criteria? – Closing the Loop – linked to program and institutional mission and goals 109
- 110. What is in place at COM-FSM? IAP Assessment Process • IAP Handbook – Background on quality instruction and services – Definition of assessment – Assessment techniques – Worksheets & directions • Improvement plan - objectives/outcomes for performance budget (worksheet #1) • Assessment plan (worksheet #2) • Assessment report – closing the loop (worksheet (#3) – Assistance with student learning outcomes and services objectives/outcomes 110
- 111. What is in place at COM-FSM? • Policy on continuous improvement cycle – Links • Strategic plan • IAP assessment • President’s retreat (priority setting) • Budget (performance) – Processes and procedures to follow at each stage – Focuses the college on continuous improvement at all levels 111
- 112. What’s remaining? Performance budgeting (putting in place) • Determines what is to be accomplished – Based on IAP improvement plan (worksheet #1) – Impacted by assessment report that determines if success criteria was achieved for key results – Closes the Loop on the improvement cycle (worksheet #3) • Allocates resources based on results to be obtained • Recognizes success and failure • Drives line item budget • Links budget items to what is to be accomplished • Basis for monitoring and reporting • Allocates time as well as dollars ($) 112
- 113. Key results/outcomes for COM-FSM Institutional & campus levels Graduation rates Based on meeting institutional, program and course student learning outcomes Retention rates Progression Persistence Transfer rates (internal & external) Course completion rates Program completers Job placement Employer satisfaction Others. 113
- 114. Quality, effectiveness and efficiency • Improvement of quality of services – Instructional techniques that promote increased student learning (meeting student learning outcomes at course, program and institutional level) – Satisfaction rates (surveys to be administered in mid October) for colleges programs and services (instructional, student and administrative services) • Students • Faculty/staff • Effectiveness and efficiency – Increased productivity (even with reduced resources) – Increased accuracy – Increased satisfaction • Rating on student services and administrative services program rubrics – Assists with setting improvement needs (student services developed, administrative services under development) 114
- 115. Roles & responsibilities • Vice President’s and Campus Directors – Ensure that the sum of instructional, student and administrative services result in improvement of key results at each campus and in each service area. – Ensure that key results/outcomes are meet – Ensures focus on clients (students, community, leaders) • IC, SSC, Office Directors – Ensure that programs and offices support key results/outcomes of the college – Continually improving quality, effectiveness and efficiency of instruction and program services – Ensures focus on clients (students, community, leaders) 115
- 116. Changes • What gets measured gets done. • If you don’t measure results, you can’t tell success from failure. • If you can’t see success you can’t reward it. • If you can’t reward success, you may be rewarding failure. • If you can’t recognize failure, you can’t correct it. • If you can demonstrate results, you can win public support. • Systems and culture must change • Push authority and flexibility to lowest levels • Aligning organizational infrastructure to support a performance management environment • Evolutionary process -- not a quick fix 116
- 117. Implementation Issues • Determine results to be obtained (quantities, high level) – Measures & data sources • Writing SMART Objectives/outcomes with by or through strategies & activities – Identify outputs for use with FSM BPS • Link to results and SMART objectives – Financial resources ($ allocation) – Human resources (time allocation) • Monitoring & reporting – Reporting accomplishments against plans – 117
- 118. Changes • Focus on results/outcomes • Accountability defined at institution, campus, program levels – Success recognized – Failure recognized – Rewards and incentives for quality work • Transparent in allocation and use of resources • All programs and services addressed • Monitoring & reporting – Accomplishments/results against plans – Measures 118
- 119. SMART goals and objectives • S = Specific • M = Measurable • A = Attainable • R = Realistic • T = Timebound 119
- 120. SMARTer, C-SMART & SMART - S SMARTer SMART objectives that are Extending Reviewed C – SMART SMART Objectives that are also CHALLENGING SMART – S SMART objectives that are also stretching 120
- 121. Types of objectives Process objectives lets you know what you are doing and how you will do it; describes participants, interactions and activities Impact objectives lets you know what the long term implications of your program[me]/ activity will be; describes the longer term impact on your target audience or organization Outcome objectives lets you know how you will change attitudes, knowledge or behavior (short term); describe the degree to which you expect this change Personal objectives SMARTer objectives are often written for project management or business and performance management, however as individuals in our personal development plans, SMARTer objectives are also a valuable formula within which to set and individual measure performance. 121
- 122. Specific S Specific Stimulating Simple Stretching Succinct Straight forward Self owned Self managed Self controlled Significant Strategic Sensible 122
- 123. Measurable M Measurable Motivating Manageable Meaningful Magical Magnetic Maintainable Mapped to goals 123
- 124. Achievable A Achievable Appropriate Actionable Attainable Ambitious Aspirational Accepted/ acceptable Aligned Accountable Agreed Adapted Assignable As-if-now Adjustable Adaptable 124
- 125. Realistic R Realistic Relevant Results Orientated Resources are adequate Resourced Rewarding Recorded Reviewable Robust Relevant to a mission 125
- 126. Timebound T Time-.. bound limited driven constrained related phased sensitive specific stamped lined Tangible- Trackable Traceable Timed/ Timely Toward what you want 126
- 127. SMARTer Extending & Reviewed E Extending Exciting Evaluated Engaging Energising Ethical Enjoyable R Reviewed Rewarding Recorded Realistic Relevant Resourced Research Based 127
- 128. Definitions Specific Measurable Achievable Realistic Time Objectives should specify what they need to achieve You should be able to measure whether you are meeting the objectives or not Are the objectives you set, achievable and attainable? Can you realistically achieve the objectives with the resources you have? When do you want to achieve the set objectives? 128
- 129. Detail Specific Acronym element Description Diagnostic Questions Specific Specific means that the objective is concrete, detailed, focused and well defined. The objective must be straight forwards and emphasize action and the required outcome. Specific also means that it’s results and action- orientated. Objectives need to be straightforward and to communicate what you would like to see happen. To help set specific objectives it helps to ask: WHAT am I going to do? This are best written using strong, action verbs such as conduct, develop, build, plan, execute, etc. This helps your objective to be action- orientated and focuses on what’s most important. WHY is this important for me to do? WHO is going to do what? Who else need to be involved? WHEN do I want this to be completed? HOW am I going to do this? What exactly are we going to do, with or for whom? What strategies will be used? Is the objective well understood? Is the objective described with action verbs? Is it clear who is involved? Is it clear where this will happen? Is it clear what needs to happen? Is the outcome clear? Will this objective lead to the desired results? 129
- 130. Detail Measurable Measurable If the objective is measurable, it means that the measurement source is identified and we are able to track the actions as we progress towards the objective. Measurement is the standard used for comparison. For example, what financially independence means to one person, may be totally different compared to what is means for another. If you cannot measure it .. you cannot manage it It’s important to have measures that will encourage and motivate you on the way as you see the change occurring, this may require interim measures. Measurements (and the visible progress) go along way to help us to know when we have achieved our objective. How will I know that the change has occurred? Can these measurements be obtained? 130
- 131. Achievable Achievable Objectives need to be achievable, if the objective is too far in the future, you’ll find it difficult to keep motivated and to strive to attain it. Objectives, unlike your aspirations and visions, need to be achievable to keep you motivated. Objectives need to stretch you, but not so far that you become frustrated and lose motivation. Can we get it done in the proposed timeframe? Do I understand the limitations and constraints? Can we do this with the resources we have? Has anyone else done this successfully? Is this possible? 131
- 132. Realistic Realistic Objectives that are achievable, may not be realistic….. however, realistic does not mean easy. Realistic means that you have the resources to get it done. The achievement of an objective requires resources, such as, skills, money, equipment, etc. to the task required to achieve the objective. Whilst keeping objectives realistic, ensure that they stretch you. Most objectives are achievable but, may require a change in your priorities to make them happen. Do you have the resources available to achieve this objective? Do I need to revisit priorities in my life to make this happen? Is it possible to achieve this objective? 132
- 133. Timebound Time Time-bound means setting a deadlines for the achievement of the objective. Deadlines need to be both achievable and realistic. If you don’t set a time you will reduce the motivation and urgency required to execute the tasks. Agreed Time frames create the necessary urgency and prompts action. When will this objective be accomplished? Is there a stated deadline? 133
- 134. Writing SMART objectives • Don't try to use that order M-A/R-S-T is often the best way to write objectives.
- 135. Writing SMART objectives • Measurable is the most important consideration. • You will know that you've achieved your objective, because here is the evidence.
- 136. Measurable • Summary: Is there something measurable to assess progress towards the objective?
- 137. Achievability • Summary: With a reasonable amount of effort and application can the objective be achieved?
- 138. Realistic • Summary: Can the people with whom the objective is set make an impact on the situation? Do they have the necessary knowledge, authority and skills?
- 139. Specific Who is going to do how much of what by when? • By September 2007, all health educators in our district will have participated in a district- wide mapping and alignment workshop. • By January, 2008 all health educators in our district will have completed an update to our k-12 health curriculum scope and sequence.
- 140. Specificity • Summary: Is there a description of a precise or specific behavior/outcome which is linked to a rate, number, percentage or frequency?
- 141. Time based • In the objective somewhere there has to be a date • (Day/Month/Year) for when the task has to be started (if it's ongoing) and/or completed (if it's short term or project related). • Simply: No date = No good.
- 142. Types of Organizations Autocratic Organization: senior leader or Founder use command and control based on assumption that they have all the answers Hierarchical Organization: chain of command is observed so that ideas are filtered or killed and a select few make it to top Learning Organization: Individuals takes responsibility for continued self development but organizing wide knowledge creation is not ultimate goal Teaching Organization: Everyone is expected to contribute to organization’s knowledge base by teaching others across boundaries Empowerment Organization: Everyone is empowered to function as per the required needs of the organization and the department he/she leads
- 143. Change at all Levels Understand Mission Statement & Vision Clarity Skills Development & Improvement by Training Incentives & Bonuses Resources, Training & Education Understanding Action Plan
- 144. Reliance On Alignment through dialogue and authority Commitment and Contribution by all Employees to strategy Vision & values Level of Knowledge creation Sharing Best practice And Knowledge Across boundaries Low Low Low Low High High High High Autocratic Organization: the senior leader or the Founder use command & control based on the Assumption that they have all the answer Hierarchical Organization: the chain of command is observed so that ideas are filtered or killed and a select few make it to the top leaders Learning Organization: Individual takes responsibility for continued self development but organizing wide knowledge creation is not the ultimate goal Teaching Organization: Everyone is expected to contribute to the organization’s knowledge base by teaching others across boundaries. Empowerment Organization: Everyone is empowered to function as per the required needs of the organization and the department he/she leads
- 145. Elements to implement successful change False Starts Vision Skills Incentives Resources Action Plan Frustration Little Change Anxiety Confusion CHANGE Skills Incentives Resources Action Plan Vision Incentives Resources Action Plan Vision Skills Resources Action Plan Vision Skills Incentives Action Plan Vision Skills Incentives Resources
- 146. Leadership Challenges • Autocratic leadership expectations – Exhausted leaders – Disempowered employees • Poor problem solving – Exhausted leaders – No accountability or responsibility taken by employees • Poor Work-Life Balance – Exhausted leaders – Exhausted employees – Less than ideal decision making
- 147. On the road to “change “ Management vs. Leadership • Innovate • Ask what and why • Focus on people • Do the right things • Develop • Inspire trust • Longer-term perspective • Challenge the status-quo • Have an eye on horizon • Originate • Are their own person • Show originality • Administer • Ask how and when • Focus on systems • Do things right • Maintain • Rely on control • Short-term perspective • Accept the status-quo • Have an eye on bottom line • Imitate • Emulate the classic • Good soldier • Copy Zaleznik - 1989
- 148. Programme Objectives Tangible & Intangible Indicators Balanced Objectives Matrix Strategies & Relations with Balanced Objectives Balanced Objectives Cards Application Balanced Objectives Road Map Measurement of Competitiveness & Quality Scale
- 149. Programme Contents Management by Objective & Concepts Delving into quality Perspective {concepts} Procedures & Operations from Quality Perspective HR& Investment for Development and Education Change from tangible to intangible indicators Balanced Objectives and Strategic Maps Matrix Scales of Procedures Competitiveness & Quality Management by objectives Delving into Quality Concept Quality & Procedures (operations) HR& Investment for Development & Education Scale for Excellence Balanced Objectives & Strategic Map Employees Performance Evaluation
- 150. Management Old Mindset Fredrik Taylor -1856 Profound Knowledge - Leadership Process - Human Resources Innovation - Learning - Change Mindset Motivate by money only Employees are lazy Fear is the only solution Do not trust employees Customers care about price only Productivity & Efficiency Hierarchy is the answer Protect local industry Management by objectives Conflict between departments Change Old mindset to escape this frame of Reference to innovate
- 151. The Madness of Management • The trouble is, some mangers believe they can carry on doing the same things, yet achieve different results, but… • If you always do what you always did, you’ll always get what you always got! The biggest enemy of sustained growth is “cultural lock-in”, the phenomenon by which managers get attracted to existing products and processes To successfully achieve the changes needed, we will require a balance of hard and soft skills. We’ll need some different behaviors. And some different thinking
- 152. Quality Profound Knowledge in Knowledge Age Industrial Age Knowledge Age Leadership Status & Promotion Selection Management Controlling Employees Authorization and enabling Structure Hierarchical & Bureaucratic Horizontal & Flexible Motivation External Internal Communication Profitable & Short Term Long Term Balanced Objective Education Top to Bottom Bottom Top Training Acquired Technical Skills Planned Training & Development Employees Costs and Charges Investment, Development Education
- 153. Balanced Scorecard Historical Lock • Industrial Revolution Age 1850 -1975 Financial indicators Product Management, Think tanks & Laborers Lack of Customer care Quality of Product Historical Perspective
- 154. Balanced Scorecard Historical Lock • Industrial Revolution Age 1850 -1975 One segment for customers Separate Sections & Procedures Separate Relations (Purchases, Manufacturing, Selling, Tangible Objectives Evaluation)
- 155. Balanced Scorecard Historical Lock • Information & Knowledge Age 1975- Date Balanced Indicators Product & Service Human Resources & Creativity Care for Customers & importers Quality of Product & Service Prospect & Compatibility
- 156. Management by Objectives (1970) • Tangible Financial Indicators • Distrust for Human Resources • Lack of Customer Care • Lack of Measuring & Developing Procedures Management by Balanced Objective (2000) Intangible Quality Indicators Human Resources Procedures Customers
- 157. Increasing Financial Value Concept for Intangible Resources in the International Organization Financial Indicators 34% Customer Indicators 22% Operations & Procedures 22% Developing & Educating Human Resources 22% Total 100% Current Evaluation of International Auditing Firms. Customers’ realization of the company influence the market value & share accounts payable & capital evaluation which influence performance and results Dow Market Value 21 Billion Dow Account Payable 8 Billion 75% of the companies Market Value are from intangible resources. Intangible resources include: Creativity, Human Resources, Customer Relations, Marketing 1984 (38%) 1994 62% 2004 75% 20yrs 10yrs 1yr
- 158. To achieve excellence..Something has to change…Mindset…Attitude..Behaviours “The significant problem we face cannot be solved by the same level of thinking which caused them “ Albert Einstein Thinking Systems Outcomes
- 159. Learning Organization • An organization that creates, acquires, transfers, and retains knowledge. It’s particularly good at changing its behaviour to reflect new knowledge and insights. Peter Senge’s five core concept (The Fifth disciplines) 1. Personal Mastery (growth driver) 2. Building Shared Vision (Develop a Common Future) 3. Team Learning (Dialogue, Skillful discussion) 4. Mental Models – hidden Assumptions & Beliefs 5. System thinking Integrate all the others, body of knowledge and tools that help people see the pattern in complex system A Learning Organization has the capability to learn new things and change the way it behaves…
- 160. Evolution of Teaching Organization Reliance On Alignment through dialogue and authority Commitment and Contribution by all Employees to strategy Vision & values Level of Knowledge creation Sharing Best practice And Knowledge Across boundaries Low Low Low Low High High High High Autocratic Organization: the senior leader or the Founder use command & control based on the Assumption that they have all the answer Hierarchical Organization: the chain of command is observed so that ideas are filtered or killed and a select few make it to the top leaders Learning Organization: Individual takes responsibility for continued self development but organization wide knowledge creation is not the ultimate goal Teaching Organization: Everyone is expected to contribute to the organization’s knowledge base by teaching other across boundaries.
- 161. Results Achieving results by Empowering, Motivating & Leading People Information Material People Money HR Money IT Material • Plan • Organize • Direct • Control • Motivate • Empower • Lead • Trust Quality Financial indicators Customer Loyalty Internal Process HR Development Balanced Scorecard Traditional Management Globalization Leading
- 162. H.R Communication Competencies (Iceberg Model) Skills • Technical • Human Relations Knowledge • Experience • Education •Training Communication 2 1 Automatic level of Communication Attitudes • Motives Behaviours • Concept • Self • Traits The power of your mind – the automatic level, the subconscious mind, When we learn something we use the conscious part, As knowledge develop it is stored in the subconscious “Attitudes” unconscious competence.
- 164. Company (HR) Effectiveness And ProfitabilitySix Sigma Balanced Scorecard Motivate Selection /Discharge /Transfer Empower Development & Coaching Cando Will do
- 165. Self Awareness & Perpetual Accuracy Performance Appraisal and it’s effect in Leadership Maturity Cause Effect Performance Appraisal Leadership Maturity Self Awareness Distorted Perception 100% 100% Reality Perception Awareness of my feeling Leadership Maturity & Self Awareness
- 166. Situational Leadership SUPPORTIVEBEHAVIOURS Empowerment Delegating Directing CoachingFacilitation 3 4 2 1 DIRECTIVE BEHAVIOURS Trust Competency Commitment
- 167. Leader Leader Leader Leader Leader Level 1 Leader Decision - Monologue Level 2 Input Leader Decision Level 3 Dialogue Leader Decision Level 4 Collaboration Level 5 Delegate Empowerment Metaloge We have decided They have decided Criteria Process LEVELS OF DECISION MAKING
- 168. Building your Talent Base – Company Capabilities Secret Formula (Excellence of Intellectual Capital) = Competence x Commitment Shared Mindset/Culture Talent Speed Learning Accountability Collaboration Quality of Leadership
- 169. Building your Competency Model 1. Assess the Competencies needed 2. Invest in Developing you People (Future Competence) 5 B’s Buy Recruiting from outside Build Train & Develop, Rotate, Action learning, Assignment Borrow New ideas (Consultant, Customer, Suppliers) Bounce Remove low performing or under performing individuals Bind Retain the most talented employees Employee Commitment VOI²C²E - V Vision - O Opportunity - I Incentives - I Impact - C Community - C Communication - E Entrepreneurship
- 170. Comprehensive Leadership of Strategic Performance Management 1. Importance of linking performance with objectives and objectives with message and message with vision. 2. Managing performance effectively and with transparency based on continuous comparativeness between the result and target. 3. Selection/designing value added procedures on scientific and practical bases considering the decrease in costs and time sparing with quality commitment 4. Caring mainly for human resources while selecting, promoting and changing their conditions and training and compensating them financially based on their performance. Vision Message Values Strategic Objectives Performance
- 171. Comprehensive Leadership of Strategic Performance Management 5. Taking the best decision quickly and with the least costs is generally the corner stone for any institution to realize its strategic objectives. Thus, it is crucial to support internal decision making by providing proper information and facilitating internal communication with the employees. 6. The availability of laws and by-laws spontaneously in any institution is per se important. Thus it is the most important elements of supporting decisions besides preserving all parties’ rights
- 172. Plan Develop Commitment Allocate Resources Educate Personnel Implement Work to Plan Collect Data Stick to Schedules Review Analyze Data Get Feedback Find Strength and Areas for Improvement Assessment Develop Targets Prioritize objectives Involve all levels RADAR Review Cycle Use Feedback Report
- 173. EFQM - RADAR Results Approach Deployment Assessment Review Defining Results Planning & Developing Methods & Tools (Approach) Generalizing & Deploying Methods & Mechanisms Methods & tools Assessment & review their Dissemination & Deployment
- 174. The Systematic Strategy Approach – Development Process 1 - Outcomes 3 - Problem 5 - Action Plan 2 - Goal 4 - Systematic Problem 6 – Current Approach 10 - Change 7 - Solution 8 - Systematic Solution 9 - Changes Inputs Process Outputs Finding Problem Process/System Thinking Correcting Problem Reflecting Thinking Generating Solutions Convergent Thinking
- 175. The Systematic Strategy Approach – Development Process Finding the Problem Correcting The Problem Generating Solutions Convergent Thinkers Deciding on Solution Implementers Divergent Thinkers System Thinkers Diverge Converge Learning
- 176. Fundamental Concept of Excellence Management by Process & Facts Result Orientation Continuous Learning Improvement by Innovation People Development & Involvement Leadership constancy of Purpose Social Responsibility Customer Focus Partnerships Development
- 177. Profitability, Customer Service & Competition Chain 1 - Institution Internal Quality Selections for Human/ Training/ Powers/ Leadership 2 – Employee Satisfaction 3 – Customer Quality & Service 4 – Customer Satisfaction 5 – Retaining Customers 6 – Institution Profit
- 178. Inputs – The Six M’s Manpower. Employee, Operator, Accountant, Sale Rep Machine. Computer, Machine, Fax, Projector Method. Standard Operating Procedure (SOP), Computer Program Measurement. Time, Defects, Money Material. Equipments, raw material, forms Mother Nature. Environment, weather, Natural Disasters Process Input Controllable (X’s) Transformation A Series of Steps that Change the Input Inputs Outputs
- 179. Variability in Processes The 6 M’s Process Component Juran Rule 94% Common Cause, Process Improvements 6% Special Causes.. Control Variation in Process Machines Material Manpower Mother Nature Measurements Methods After BPR Before BPR Process Drivers Quality Cost Speed Service
- 180. Process Improvement Path PLAN: 1- Team Formation 2- Purpose & Objectives 3- Analyze Current Situations 4-Develop Improvements ACT: 7- Standardize & Monitor 8- Review 9- Future Planning CHECK: 6- Evaluate the Pilot DO: 5- Implement the Pilot ACT PLAN WORK PROCESS CHECK DO Gather data Interpret Data Translate to Matrix Gap Analysis Take Action Review against Plan Measure Effectiveness Our Performance level
- 181. Improving a Problem Statement & Goal Original Statement – S M A R T “We need to improve Customer Satisfaction” Specific Retail customers have been complaining about incomplete shipments Measurable 10% of shipments are incomplete Achievable We observe several weeks with only 3% incomplete shipments. One week with 1% Relevant Customer complaints will lead to a loss of business Time Bound Reduce complaints within 2 months Evaluate Monitor progress regularly – milestones Reversible Reset your goals in case of failure to achieve difficult goals, or injury
- 182. Revised Problem Statements and Goal S M A R T E R “ Presently 10% shipments are incomplete (double our industry average), Several of our customers have threatened to stop doing business with us” The team will reduce incomplete shipments from 10% to 3% within 2 months Risk Management Definition: “The combination of probability of an event and its consequence” The ability to master Risks by minimizing Threats and maximizing Opportunities
- 183. The Planning Process One hour spent is worth four hour of execution 1 - Should Be 2 - As is 3 - Goals 4 - Action steps 5 - Cost 6 - Timetables - Schedule 7 - Implementation 8 - Follow Up
- 184. 3 types of Business Process Top Management Processes Core Operational Processes Internal Support Processes Shareholder’s Need Regulations Competitors Activity Internal Customers Need Internal Customers Satisfaction External Customers Need Strategies, Objectives & Control External Customers Satisfaction
- 185. The Planning Process Strategic Thinking Long Range Planning Tactical Planning Values Mission Vision Strategy HR Key Strategic Areas Critical Issue Analysis Long Term Objectives Strategic Action Plans Key Results Areas Critical issue Analysis Key Performance Indicators Objectives Action Plans Plan Review
- 186. Strategy Planning processes vs. Scenario Planning (New Mindset) • Managing uncertainty – Problem: Choosing and following direction curing time of uncertainty – Solution: Imagine possible futures, then make a strategic decisions. – Map scenario to the future • Strategy in Motion (make decisions, move forward recognizing that decision may be wrong) – a deliberate plan of action – a continuous process – Reactive or Proactive
- 187. Strategy Planning processes vs. Scenario Planning (New Mindset) • Strategic Visioning Process – Imagine end-state scenario – Identify events for each end-state – Map scenario to the future Scenario Planning Methodology is used for Strategic Visioning, this methodology differs from the Strategy Planning processes in that it encourages future and visionary thinking to identify possibilities going forward There are three basic components to the Strategic Vision: • End-States • Events • Scenarios that describe the sequence of events necessary to achieve a possible end-state.
- 188. Strategic Analysis Process Customer value Needs Assessment Market Review SLRP Strategies Competitive Strategy Workshops Roadmaps Future SLRP Topics POR Plan of Records Strategic Vision/ Responses
- 189. What you can measure, you can manage Measure Metrics Indicators Performance Measure Business Planning Strategic Thinking Are we doing things right? Are we doing the right things? Input Process Output Outcome
- 190. How did they do it? They created “Strategy- Focused Organizations” Strategy: they made strategy the central organization agenda Focused: they created incredible focus on the strategy Organization: they mobilized their employees to act in fundamentally different ways, guided by the strategy Strategy Management Process
- 192. Strategy Mission Statement & BSC Strategy is a Series of Assumptions, Questions, “What If Cause and Effect Logic. If we upgrade human resources by training and knowledge (cause), emphasis should be on improving and developing product quality and service. When improving procedures (quality, costs, and time process) (cause) emphasis should be on improving customer service. This means providing services and commodities on time and with required quality and price would affect customers’ loyalty which if takes place will influence the financial, profit and competitiveness results……...Cards of Balanced Objectives Measurements.
- 193. Strategy Mission Statement & BSC Mission Strategy BSC Balanced Objectives are the realization of task and vision into future scenario through strategic management and intangible performance measurement and the main objective is perpetual change, success, distinction and excellence.
- 194. Business Performance Drivers (Competence & Commitment) HR Performance Drive Business Performance (Competence & Commitment) Performance Development Leadership Culture Involvement Structure
- 195. Skill & Knowledge to drive Business Performance BSC & Strategy Willing to use skill & Knowledge to achieve Strategy, BSC & Strategy Secret Formula Commitment X Competence
- 196. Integrated Solution for Hierarchical System Problems Balanced Measurements, Quality, Resisting Change, influencing behavior and morale Strategic Balanced Scorecard Financial Indicators Management Balanced Objectives Strategy Human Resources Analysis Human Resource Capital Customer Relations Management Customer Relations Balanced Process, Perpetual improvements & by-laws management
- 197. Strategy Management Overview Knowledge Results Action Process Management Change Management Industry Analysis Scenario Planning Strategic Operational Experience Balanced Scorecard Strategic Architecture Scorecard Design
- 198. What do Managers need to know in order to take the Actions that lead to the right business Results?
- 199. From Strategic Architecture to BSC Strategic Initiatives Customers Financial Internal Learning Internal Perspective External Perspective External Perspective Internal Perspective Core Capability Internal Processes Strategic Assets Core Competence Customer Value Case Customer Value Proposition Economic Value Case
- 200. Outside in Thinking Customer Process B C Company Process The Eye of the Beholder View Company Contribution Company Traditional View of its Contribution
- 201. Customers are why companies implement quality (BSC) Expect Performance, Reliability, On-time Delivery, Service, Competitive Prices etc. See and Feel the results – not just Hearing about BSC results
- 202. Quality means = Knowledge = Measurements Transforming knowledge into Vision & Values We don’t know what We don’t know We can’t do what we don’t know We wouldn’t know until we measure We don’t measure what we don’t value We don’t value what we don’t measure The knowledge of measuring the hidden cost of Quality!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! You cannot Change what you cannot measure (Measure Process)
- 203. 3 – Transfer Behavior 4 levels of Evaluation (ROI) each successive evaluation level is built on information provided by the lower level. Did trainee like it? Trainee Perception & Attitude Did Trainee learn? Skills, knowledge & Attitudes Learning Objectives Did Trainee use it? Applying newly acquired skills, knowledge or attitude to work place Did it impacts BSC? Impact DED performance, ROI, Quality, waste reduction, HR moral satisfaction, absenteeism, profit, safety. Supplier: Trainer Trainee: HR Process: Training Delivery Quality: Effectiveness Supplier Training Delivery DED-HR Assessing Training Effectiveness Kirkpatrick’s Four – Level Evaluation Model 1 - Reaction 2 - Learning 4 – BSC Results
- 204. Translating the Balanced Scorecard into Objectives & Measures (Putting it Together)
- 205. Balanced Scorecard Components (Relation & Linking) Initiatives Required Programmers for Objectives Realization Target Performance Indicators Measure Success Measurements Objectives Objective of backing strategic decision for success Balanced Objectives & Measurement Strategy Promotion & Success Societies Researchers Marketing Tactics Programme A 10% Programme B 40% Programme C 50% Programme Mixture Optimal Exploitation Budget Benefits for good customers Customer’s club Forum 95% Customers’ Participation Increasing Customers’ Loyalty Customers Research & Development Programmes 2005-15% 2006-50% 2007-60% Deployment of New Programmes Developing new Programmes Operations - Customer Relation Training - Knowledge Management - Employees Development 90% Dual skill Training Developing Strategic Skills Development of Human Resources
- 207. Deployment & Initiating Change Continuous Performance Assessment and Development & Strategic Balanced Performance Assessment 1. Evaluating internal & external status quo by work team. 2. Developing Main Strategies to action plan by various head sectors. 3. Transforming strategies to action plans for sectors and identifying balanced objectives. 4. Reaching a strategic map for the company 7 clarifying relations among sectors for balanced indicators by beneficiaries (customers-employees- importers). 5. Performance indicators measurements & their development for strategic planning and operational plans follow-up. Coordinating with the quality sector for assessing process in the company. 6. Recognizing deployment obstacles and avoiding them for successful deployment.
- 208. Deployment & Initiating Change Continuous Performance Assessment and Development & Strategic Balanced Performance Assessment Procedures 1. Analysis & strategic planning. 2. Strategy of objectives and balanced indicators 3. Implementation in all sectors & measuring process and its efficiency 4. Follow-up, assessment, improvement & reviewing outcome & indicators. The ultimate goal is to achieve a strategy by measurement of outcome and balanced indicators to influence behavior.
- 209. Deployment & Initiating Change Continuous Performance Assessment and Development & Strategic Balanced Performance Assessment Assessment Implementation Planning Deployment
- 210. Translate the Strategy to Operational Terms Organization Learning “To achieve my vision, how must my organization learn & improve?” Internal Perspective “To satisfy my customer, at which processes must I excel?” Customer Perspective “To achieve my vision, how must I look to my customers?” Financial Perspective “If we succeed, how will we look to our shareholders?” The Strategy
- 211. Measurement is the language that gives clarity to vague concepts Measurement is used to communicate, not to control Strategy can be described as a series of cause & effect relationships
- 212. Align the Organization Around the Strategy
- 213. Make Strategy Everyone’s Job 95% of the typical work force does not understand the strategy CORP SBU The Strategy Focused Workforce • Education • Personal Goal Alignment • Balanced Paychecks Bottom-Up Process to Internalize & Execute the Strategy Top-Down “Bringing Process” to share the strategy & align the workforce
- 215. Make Strategy A Continual Process The Problem: The Strategic Management Process is missing in most organization Strategy Balanced Scorecard Budget Performance 92% of organizations do not report on lead indicators 85% of management teams spend less than one hour per month on strategy issue 78% of organizations luck Budgets to an annual cycle 20% of organization take more than 16 weeks to Prepare a budget 60% of organizations don’t link strategy & budgets Strategic Learning Loop Management Control Loop
- 216. Leadership Alignment – For quality transformation Vision Method Relationship D A T A People Leaders Customers Companies
- 217. Six Issues of a Successful Scorecard Interfaces Strategy Map Roles IT Support Dialogue Incentives
- 218. The attraction of Balanced Scorecards is to help translate strategy into stories business logic and tasks that grab people’s imagination and so results in purposeful action. Yet too often it hasn’t worked that way.
- 219. Strategy Map – Balanced Scorecard Perspective Financial Customer Process Development Establish new markets Improve Staff Skills Improve Technology Increase Customer Service Increase Efficiency Increase Customer base More Satisfied customers Stronger Finance Improve Profitability
- 221. Effective Team Work Stages of Team Development 3 - Norming 4 - Performing 2 - Storming 1 - Forming
- 222. What makes a Good Project Team? Effective Project Team Trust & respect Communication Conflict Resolution Roles & Responsibility SynergyLeadership
- 223. Resistance to change Key staff not available Unrealistic timescales, business can’t cope Solution is not adopted, ‘not invented here’ ‘To be’ is not achieved Lack of ownership Project takes Longer & costs more Sponsors support in public but not in private Lack of enthusiasm & support from the business Project not properly Planned or resources Repeat past mistakes Confusion and mixed messages, criticism, the rumour mill Nobody takes responsibility Staff not properly trained or educated, performance worsens Why worry about Business change?
- 224. Elements required to implement successful change False Starts Vision Skills Incentives Resources Action Plan Frustration Little Change Anxiety Confusion CHANGE Skills Incentives Resources Action Plan Vision Incentives Resources Action Plan Vision Skills Resources Action Plan Vision Skills Incentives Action Plan Vision Skills Incentives Resources
- 225. Change at all Levels Understand Mission Statement & Vision Clarity Skills Development & Improvement by Training Incentives & Bonuses Resources, Training & Education Understanding Action Plan
- 226. Examples • Campus retention rate will increase to 60% from Fall 2009 to Fall 2010 by: – Strategy 1 – Strategy 2 • Campus graduation rate will increase to 10% for Fall 2007 cohort by: – Strategy 1 – Strategy 2 226
- 227. Examples By the end of the asthma management classes, 75% of patients will be able to describe and demonstrate the correct use of a Peak-Flow Meter. By May 10, 2009 the Health Education staff from the Stroke Association will have planned and conducted 4 skills building workshops for 50 carers of recently diagnosed Stroke patients at the Chiswick training centre. Profitability Objectives - To achieve a 25% return on capital employed by August 2009. Market Share Objectives - To gain 25% of the market for sports shoes by September 2009 Promotional Objectives - To increase awareness of the dangers of flowers in Wales from 12% to 25% by June 2009. To increase trail of X washing powder from 2% to 5% of our target group by January 2009. 227
- 228. Exercise 1. What are your priorities? 1. Review strategic plan 2. Review improvement plans 3. Review assessment reports 2. What measures are appropriate for your area? 1. Review balanced scorecard 2. Review assessment plan 3. Write SMART objectives plus strategies based on your priorities and measures. 228
- 229. Exercise • What resources are needed to accomplish your improvement plan SMART objectives/outcomes? – Human – Financial 229
- 230. What Have You Learned? • How are job objectives different from job tasks? How are they different from job descriptions? • What about the SMART model do you find most useful? How do job objectives drive your work? • How do you identify the right measures to use in an objective? Why have multiple measures? • Why is alignment of job objectives to organizational goals so important in NSPS?
- 231. 231 Summary Although the terms “goals” and “objectives” are often used interchangeably, there are significant differences: – Goals are general, intangible, broad, abstract, and long-range directions generally set by top executives – Objectives are specific, measurable, narrow, concrete, and are short-range plans generally set by managers to accomplish goals.
- 232. 232 Summary cont’d. • Setting goals and objectives is important because it is the first and most critical step in the planning process. • Under our MBO process, top management sets our corporate goals. Managers use these goals to set department objectives, their own objectives and their employees’ objectives.
- 233. 233 Summary cont’d. At (name of company) we set SMART Objectives S Specific M Measurable A Achievable R Realistic T Time-oriented
