Presentation1.pptx, radiological anatomy of the naso, oro and hypopharynx.
- 1. Radiological anatomy of the naso, oro and hypopharynx. Dr/ ABD ALLAH NAZEER. MD.
- 2. Anatomy of the pharynx Compartments.
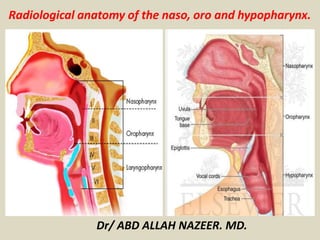
- 3. Anatomy of the pharynx. The pharynx extends from the nasal cavity to the larynx and is arbitrarily divided into three compartments. The nasopharynx extends from the skull base to the soft palate. Its function is entirely respiratory, and the nasopharynx is not considered further in this chapter. The oropharynx is posterior to the oral cavity and extends from the soft palate to the hyoid bone. The hypopharynx (laryngopharynx) extends from the hyoid bone to the cricopharyngeus muscle. The base of the tongue forms the anterior boundary of the oropharynx. The outline of the surface of the tongue is nodular because of the presence of lymphoid tissue forming the lingual tonsils and the circumvallate papillae, which contain taste buds. The lingual tonsils may hypertrophy and mimic a neoplasm. The epiglottis and aryepiglottic folds separate the larynx from the oropharynx and the hypopharynx. The valleculae are two symmetrical pouches formed in the recess between the base of the tongue and the epiglottis. They are divided medially by the median glossoepiglottic fold and bounded laterally by the lateral glossoepiglottic folds. The piriform sinuses are deep, symmetrical, lateral recesses formed by the protrusion of the larynx into the hypopharynx.
- 4. The nasopharynx The nasopharynx is that part of the pharynx between the posterior choanae and the lower limit of the soft palate. It communicates anteriorly with the nasal cavity and inferiorly with the oropharynx. The roof of the nasopharynx is bound to the inferior surface of the sphenoid and clivus by the pharyngobasilar fascia. It has the parapharyngeal space and the deep soft tissues of the infratemporal space laterally. Posteriorly it lies on the upper cervical vertebrae and longus collis and capitus, and posterolaterally the styloid muscles separate it from the carotid sheath. The eustachian tube opens on to the lateral wall of the nasopharynx on either side, piercing the pharyngobasilar fascia. This opening has a posterior ridge formed by the cartilaginous end of the tube known as the torus tubarius. Behind these ridges are the paired lateral pharyngeal recesses, also known as the fossae of Rosenmüller. The muscular layer of the nasopharynx is formed by the superior pharyngeal constrictor. The palatal muscles arise from the base of the skull on either side of the eustachian tube. The levator veli palatini accompanies the eustachian tube, piercing the pharyngobasilar fascia before inserting into the posterior part of the soft palate.
- 5. The tensor veli palatini runs around the nasopharynx and hooks around the pterygoid hamulus before inserting into the membranous part of the soft palate. These muscles, along with those in the palatopharyngeal arch, elevate the soft palate, closing it against a muscular ridge in the superior constrictor muscle (known as the Passavant ridge) during deglutition, thereby isolating the nasopharynx from the oropharynx. Lymphoid tissue lines the nasopharynx, and this is prominent superiorly where it forms the adenoids. The lymphatic drainage of the nasopharynx and related spaces is to the jugular chain of lymph nodes, especially the jugulodigastric node, which lies at the angle of the mandible. Spaces related to the nasopharynx The parapharyngeal space is a slit-like space just lateral to the nasopharynx extending down from the base of the skull. The space is bounded by the buccopharyngeal fascia. This fascial plane separates the pharyngeal muscles from the muscles of mastication (the pterygoids and the deep part of the temporalis muscle). It is loosely applied to allow movement and contains branches of the external carotid artery, pharyngeal veins and mandibular nerve. Posteriorly, it is separated from the carotid sheath by the styloid process and its muscles, and the deep part of the parotid gland lies laterally.
- 6. The infratemporal space lies lateral to the nasopharynx and paranasopharyngeal space behind the posterior wall of the maxilla. It extends from the base of the skull to the hyoid bone, and contains the pterygoid muscles. It is continuous superiorly with the temporal fossa through the gap between the zygomatic arch and the side of the skull. Medial to this, the roof is formed by the inferior surface of the middle cranial fossa and is pierced by the foramen ovale and foramen spinosum. Laterally, the space is bounded by the zygomatic arch, temporalis muscle, ascending ramus of mandible and its coronoid process. Medially, the space is limited by the lateral pterygoid plate and nasopharynx. The space lies anterior to the deep part of the parotid, the styloid process and its muscles, and the carotid artery and jugular vein. The anteromedial limit of the infratemporal space is formed by the junction of the lateral pterygoid plate with the posteromedial limit of the maxilla superiorly and the posterior border of the perpendicular plate of the palate inferiorly. The anterior and medial walls of the space meet inferiorly but are separated superiorly by the pterygomaxillary fissure, where the pterygoid plates diverge from the posterior wall of the maxilla.
- 7. The pterygopalatine fossa is a medial depression of the pterygomaxillary fissure lying just below the apex of the orbit between the pterygoid process and the posterior maxilla. Its medial margin is the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone. It is important as it connects several spaces and may facilitate the spread of pathology between them. It communicates superiorly with the orbit through the posterior part of the inferior orbital fissure. The foramen rotundum opens into it superiorly, connecting it with the middle cranial fossa. Laterally it communicates freely with the infratemporal fossa. Medially the space communicates with the nasal cavity via the sphenopalatine foramen in the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone, and with the oral cavity through the greater palatine canal, which runs inferiorly between the palatine bone and the maxilla. The fossa contains the maxillary division of the fifth cranial nerve, which runs through the foramen rotundum and into the orbit via the inferior orbital fissure. It also contains the pterygopalatine segment of the maxillary artery, which makes a characteristic loop and gives off branches to the middle cranial and infratemporal fossae and to the nasal cavity, palate and pharynx.
- 9. Lateral radiograph of the neck: soft-tissue view showing pharynx and larynx
- 12. 1 – Nasopharynx. 2 - Tensor veli palatini. 3 - Levator veli palatini. 4 - Temporalis muscle Medial / deep head. 5 - Temporalis muscle lateral / superficial head. 6 - Coronoid process of mandible. 7 - Lateral pterygoid muscle. 8 - Condylar process of mandible. 11 - Pterygomaxillary fissure.
- 65. The oropharynx and laryngopharynx The oropharynx is the part of the pharynx that extends from the lower part of the soft palate to the epiglottis. It is continuous through the posterior fauces with the oral cavity and with the laryngopharynx below. It is lined by mucosa which is continuous with that of the oral cavity and nasopharynx. Its submucosal layer is continuous with the pharyngobasilar fascia above, and its muscular layer has contributions from the superior constrictor, some of the tongue muscles, and levator and tensor veli palatini. The laryngopharynx is the part of the pharynx that lies behind the larynx. It extends from the level of the epiglottis to the level of C6, where it continues as the oesophagus. The upper laryngopharynx is moulded around the proximal part of the larynx, forming two deep recesses on either side known as the piriform fossae. During deglutition the epiglottis helps conduct fluid and solid boluses along the piriform fossae from the oropharynx to the oesophagus, avoiding the entrance to the larynx.
- 66. Oropharynx: The oropharynx lies behind the oral cavity, extending from the uvula to the level of the hyoid bone. It opens anteriorly, through the isthmus faucium, into the mouth, while in its lateral wall, between the Palatoglossal arch and the Palatopharyngeal arch, is the palatine tonsil.[2] The anterior wall consists of the base of the tongue and the epiglottic vallecula; the lateral wall is made up of the tonsil, tonsillar fossa, and tonsillar (faucial) pillars; the superior wall consists of the inferior surface of the soft palate and the uvula. Because both food and air pass through the pharynx, a flap of connective tissue called the epiglottis closes over the glottis when food is swallowed to prevent aspiration. The oropharynx is lined by non-keratinised squamous stratified epithelium. The HACEK organisms (Haemophilus, Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Cardiobacterium hominis, Eikenella corrodens, Kingella) are part of the normal oropharyngeal flora, which grow slowly, prefer a carbon dioxide-enriched atmosphere, and share an enhanced capacity to produce endocardial infections, especially in young children. Fusobacterium is a pathogen.
- 103. (Hypopharynx )Laryngopharynx: The laryngopharynx, (Latin: pars laryngea pharyngis), is the caudal part of the pharynx; it is the part of the throat that connects to the esophagus. It lies inferior to the epiglottis and extends to the location where this common pathway diverges into the respiratory (larynx) and digestive (esophagus) pathways. At that point, the laryngopharynx is continuous with the esophagus posteriorly. The esophagus conducts food and fluids to the stomach; air enters the larynx anteriorly. During swallowing, food has the "right of way", and air passage temporarily stops. Corresponding roughly to the area located between the 4th and 6th cervical vertebrae, the superior boundary of the laryngopharynx is at the level of the hyoid bone. The laryngopharynx includes three major sites: the pyriform sinus, postcricoid area, and the posterior pharyngeal wall. Like the oropharynx above it, the laryngopharynx serves as a passageway for food and air and is lined with a stratified squamous epithelium. It is innervated by the pharyngeal plexus. The vascular supply to the hypopharynx includes the superior thyroid artery, the lingual artery and the ascending pharyngeal artery. The primary neural supply is from both the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves. The vagus nerve provides a branch termed "Arnolds Nerve" which also supplies the external auditory canal, thus hypophayrngeal cancer can result in referred otalgia. This nerve is also responsible for the ear-cough reflex in which stimulation of the ear canal results in a person coughing.
- 104. The Hypopharynx Anatomy. • Hypopharynx • Pyriform sinus. • Posterior wall. • Postcricoid region.
- 105. Pyriform sinus. • Between • Inner thyrohyoid membrane • Thyroid cartilage • Lateral AE fold • Posterior wall • Inferior continuation of posterior oropharynx wall
- 106. • Postcricoid region • Anterior wall of lower hypopharynx.
- 107. Hyoid, thyroid and cricoid cartilages.
- 108. AP and lateral views of the barium-coated pharynx and hypopharynx obtained during phonation demonstrates normal anatomy but also aspiration of barium into the larynx and trachea.
- 113. Supraglottis.
- 114. 1. Hyoid bone. 2. Epiglottis. 3. Lt sternocleidomastoid muscle. 4 Lt internal jugular vein. 5. Lt internal carotid artery. 6. Lt external carotid artery. 7. Rt external jugular vein. 8. Rt & Lt piriform fossa* (recesses) 9. Tongue. 10. Rt submandibular gland.
- 115. Thank You.
