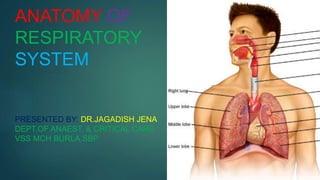
Anatomy of respiratory system
- 1. ANATOMY OF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM PRESENTED BY: DR.JAGADISH JENA DEPT.OF ANAEST. & CRITICAL CARE VSS MCH BURLA,SBP
- 2. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM CONSISTS OF : >UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT(NOSE TO LARYNX) >LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT(TRACHEA ONWARDS) CAN ALSO BE DIVIDED IN TO: >Conducting portion transports air. - Includes - Nose Nasal cavity Pharynx Larynx Trachea From the primary bronchi to the terminal bronchioles >Respiratory portion carries out gas exchange. - Composed of small airways called respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts as well as air sacs called alveoli .
- 4. Nose Provides airway Moistens and warms air Filters air Resonating chamber for speech Olfactory receptors
- 5. EXTENAL NOSE *Its upper one third is bony and lower two third are cartilaginous *Bony part consists of two nasal bones which meet in midline. *Cartilaginous part consists of -Upper lateral cartilage:extends from under surface of nasal bones above to alar cartilages below. -Lower lateral cartilage(alar cartilage):it s u shaped -Lesser alar cartilage(sesamoid):lie above and lateral to alar cartilages. -Septal cartilage *Muscles of nose: Procerus,nasalis,levator labii superioris,alaque nasi,ant. And post. dilator nares,depressor septi. These muscles help in movement of nose.
- 7. INTERNAL NOSE Divided in to –Vestibule of nose -Nasal cavity proper Vestibule of nose: Ant. and inferior part of nasal cavity lined by skin and contains sebaceous glands,hair follicles and hair called vibrissae
- 8. Nasal cavity proper: It has lateral wall medial wall floor roof *Lateral wall: Marked by three scroll like bony projections called turbinates or conchae,known as inferior,middle,superior from below upwards : Below and lat.to each turbinate corresponding meatus present. >Inferior meatus -nasolacrimalmal duct opens in to it >Middle meatus-maxillary sinus,frontal sinus,ant.ethmodal sinus opens in to it. >Superior meatus-post.ethmoidal sinus opens in to it Sphenoid sinus opens in to sphenoethmoidal recess.
- 10. APPLIED ANATOMY: 1-The inferior turbinate usually limits size of nasotracheal tube 2-Prolonged nasotracheal intubation has most often associated with infection of maxillary sinus *Medial wall: Nasal septum form the medial wall :Has highly vascular little’s area in the antero inferior part of nasal septum APPLIED ANATOMY: 1-This is the commonest site of epistaxis 2-As it is highly vascular,nasal vasoconstrictor is used to shrink the mucosa and dilate airway during nasotracheal intubation.
- 11. *Floor: Formed by palatine process of maxilla,palatine bone : Almost perpendicular to the plane of face.so tube should be inserted perpendicular to the plane of face. *Roof: Formed by nasal bones sphenoid bone,cribiformplate of ethmoid APPLIED ANATOMY: 1-Disruption of cribiform plate leads to csf rhinorrhea,is a contraindication for positive pressure ventilation as it m leads to entry of infection. 2-Is also contraindication for nasotracheal intubation,nasogastric tube insertion.
- 12. LINING OF NOSE: Vestibule- Lined by stratified squamous epithelium Respiratory region- Lined by pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium NERVE SUPPLY: a-Olfactory nerves b-Nerves of common sensation-ant.ethmoidal nerve,sphenopalatine nerve,infra orbital nerve c-Autonomic nerves
- 13. BLOOD SUPPLY: Both the internal and external carotid system supply nose. ORAL CAVITY *Extends from mouth opening to ant.tonsillar pillar *Tongue is a muscular organ which makes up most of the floor of oral cavity * Tongue has the habit of falling back on the oro pharynx & block the air passage,whenever the muscle tone is decreased (Sleep, Decreased Level of consciousness or General anesthesia ). CLINICAL IMPORTANCE: Mallampati grading helps in assessment of airway during PAC.
- 14. ORAL CAVITY Mallampatti’s Classificaton Faucial Pillar Uvula Soft palate Hard palate Uvula Soft palate Hard palate Soft palate Hard palate Hard palate
- 15. APPLIED ANATOMY: Previously it has been thought that upper airway obstruction occur due to tongue fall but recently various studies shows that airway obstruction occur mostly at the level of soft palate & epiglottis during sedation and GA.
- 16. PHARYNX *It is 12-15 cm long. *Widest at the level of hyoid bone,narrowest at the level of oesophagus. *The wall of pharynx contain two layer of muscle-Circular(external) -Longitudinal(internal) *Internal layer muscles-Stylopharyngeus,salpingopharyngeus,palatopharyngeus They elevate the pharynx and shortens the larynx during deglution. *External layer muscles-Superior constrictor,middle constrictor,inferior constrictor They advance the food from oropharynx to oesophagus. *The constrictors are innervated by pharyngeal plexus formed by-Vagus -Glossopharyngeal -External branch of sup.laryngeal nerve The inferior constrictor also innervated by recurrent laryngeal nerve.
- 17. *The internal layer innervated by glossopharyngeal nerve. *The pharynx divided in to -Nasopharynx -Oropharynx -Laryngopharynx *Nasopharynx- It extends from posterior nasal aperature to the posterior pharyngeal wall above the soft palate. APPLIED ANATOMY: Adenoids are located in its roof – which are frequently hypertrophied during childhood & may cause obstruction or hemorrhage while passing any tube through the nose.
- 18. * Oropharynx: Extends from soft palate to epiglottis Most important area in terms of airway obstruction & management as it is made of collapsible soft tissue all around. *Laryngo pharynx: Extends from superior border of epiglottis to inferior border of cricoid cartilage WALDEYER’S RING The adenoid, palatine tonsil, Lingual tonsil & tubal tonsil form a somewhat continuous circle of lymphoid tissue around the lumen of pharynx which is known as Waldeyer’s Ring. It helps in defensive mechanism of the respiratory and alimentary system by preventing the entry of micro-organisms from the external enviroment. CLINICAL IMPORTANCE: 1.This structure when infected & enlarged causes airway obstruction & impedes the passage of nasotracheal tube.
- 19. 2.Lingual tonsil hypertrophy is usually asymptomatic,has ben reported to cause unanticipated difficult intubation and fatal airway obstruction.
- 20. LARYNX *It lies in the midline of neck opposite C3 to C6 vertebra in adult & C1 to C4 vertebra in children. * It extends from the upper border of epiglottis to lower border of cricoid cartilage. *Measurements: MALE FEMALE Vertical Length - 44mm 36mm Transverse diameter – 43mm 41mm A-P diameter - 36mm 26mm *The glottis is the narrowest part in adult. *The subglottis(cricoid ring) narrowest part in children up to the age of 5 yrs. APPLIED ANATOMY That s why in children uncuffed endotracheal tube can be used.
- 21. *Larynx consists of 3 paired cartilages and 3 unpaired cartilages. *Unpaired cartilages - Thyroid - Cricoid - Epiglottis *Paired cartilages - Arytenoid - Corniculate - Cuneiform *Thyroid cartilage is the largest cartilage *Cricoid cartilage is the only complete cartilaginous ring in airway.
- 24. Muscles of larynx Intrinsic muscles of larynx: Muscle Function 1.Posterior cricoarytenoid 1.Abductor of vocal cords 2.Lateral cricoarytenoid 2.Adducts arytenoids closing glottis 3.Transeverse arytenoid 3.Adducts arytenoids 4.Oblique arytenoid 4.Closes glottis 5.Aryepiglottic 5.Closes glottis 6.Vocalis 6.Relaxes the cords 7Thyroarytenoid 7.Relaxes tension cords 8.Cricothyroid 8.Tensor of the cords
- 25. Extrnsic muscles of larynx: Muscle Function 1.Sternohyoid 1.Indirect depressor of the larynx 2.Sternothyroid 2.Depresses the larynx 3.Thyrohyoid 3.Depresses the larynx 4.Thyroepiglottic 4.Inversion of aryepiglottic fold 5.Stylopharyngeus 5.Assists folding of thyroid cartilage 6.Inferior pharyngeal constrictor 6.Assists in swallowing
- 26. NERVE SUPPLY OF LARYNX SENSORY – Above the vocal cord – Superior laryngeal nerve Below the vocal cord - Recurrent laryngeal nerve MOTOR – All intrinsic muscle of the larynx are supplied by RLN except cricothyroid which is supplied by external laryngeal nerve which is a branch of SLN. Both SLN & RLN are branches of vagus nerve
- 28. ARTERIAL SUPPLY & VENOUS DRAINAGE ABOVE THE VC - Superior laryngeal artery, a branch of superior thyroid artery. Superior laryngeal vein, drains into superior thyroid vein BELOW THE VC – Inferior laryngeal artery, a branh of inferior thyroid artery. Inferior laryngeal vein, drains into Inferoir thyroid vein. LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE ABOVE THE VC - Pre laryngeal & Jugulo – Digastric LN. BELOW THE VC – Pre tracheal & Para tracheal LN.
- 29. Function of larynx: 1. Produces vocalizations (speech) 2. Provides an open airway (breathing) 3. Switching mechanism to route air and food into proper channels Closed during swallowing Open during breathing
- 30. APPLIED ANATOMY: 1.Effects of laryngeal nerve injury on the voice: Sup.laryngeal nerve unilateral minimal effects bilateral hoarseness,tiring of voice Rec.laryngeal nerve unilateral hoarseness bilateral: acute stridor,resp.distress chronic aphonia Vagus nerve unilateral hoarseness bilateral aphonia 2.In complete paralysis of both recurrent and SLN the cords are held in mid position(cadaveric position) 3.Cords are also in cadaveric position during GA with muscle relaxants.
- 31. 4.Laryngoscopic view of larynx:
- 32. Cormack & Lehane graded laryngoscopic view as below which helps in assessment of intubation: Grd 1: Visualization of entire vocal cords Grd 2: Visualization of posterior part of laryngeal apereture Grd 3: Visualization of epiglottis Grd 4: No glottic structure seen
- 33. Assesment of ease of intubation from grading: Grd 1: No extrinsic manipulation of the larynx required Grd 2: External manipulation of the larynx is required Grd 3: Intubation possible when aided by a stylet Grd 4: Failed intubation
- 34. TRACHEA *Starts from cricoid ring(c6) to carina(t5) *Length 10-16 cm *Consists of 16-20 incomplete rings *External diameter of trachea Male: 2.3cm coronally 1.8cm sagitally Female:2cm coronally 1.4cm sagitally *Internal diameter 1.2 cm *It s flattened posteriorly and contains 16-20 horse shoe shaped cartilaginous rings *The post.part of trachea void of cartilage,consists of membrane of smooth muscle and fibro elastic tissue joining the ends of cartilage.
- 35. *The rings are incomplete to allow the trachea to collapse slightly so that food can pass down the oesophagus. *At the 6th ring trachea becomes intrathoracic *Divided into rt and lt main bronchus at carina *Distance from upper incisor to carina 28-30cm *Trachea lined by pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
- 36. 36 Trachealis muscle can decrease diameter of trachea Esophagus can expand when food swallowed Food can be forcibly expelled Wall of trachea has layers common to many tubular organs – filters, warms and moistens incoming air Mucous membrane (pseudostratified epithelium with cilia and lamina propria with sheet of elastin) Submucosa ( with seromucous glands) Adventitia - connective tissue which contains the tracheal cartilages)
- 37. 37
- 38. 38 Carina* Ridge on internal aspect of last tracheal cartilage Point where trachea branches (when alive and standing is at T5) Mucosa highly sensitive to irritants: cough reflex *
- 39. VARIOUS MEAN DISTANCES IN ADULTS OF INTEREST TO THE ANAESTHESIOLOGIST: 1.Mean distance from lips to carina: male 35.2cm female 28.5cm 2.Mean distance from nose to carina: male 31cm female 28.4cm 3.Mean distance from lips to vocal cords: male 12-16cm female 10-14cm 4.Mean distance from upper edge of larynx to lower edge of cricoid: 4-6cm 5.Mean length of trachea (vocal cord to carina): Male 12-14cm Female 10-12cm
- 40. *Dichotomous division starting with tachea and ending in alveolar sac.
- 41. 41 Bronchial tree bifurcation Right main bronchus (more susceptible to aspiration) Left main bronchus Each main or primary bronchus runs into hilum of lung posterior to pulmonary vessels 1. Oblique fissure 2. Vertebral part 3. Hilum of lung 4. Cardiac impression 5. Diaphragmatic surface (Wikipedia)
- 42. RIGHT MAIN BRONCHUS LEFT MAIN BRONCHUS 1.Shorter(2.5cm) 1.Longer(5cm in man,4.5cm in woman 2.Wider 2.Narrower 3.Angle with vertical 25 degree 3.Angle is 45 degree 4.Aorta arches over the left main bronchus
- 43. APPLIED ANATOMY: 1.Due to shorter wider and less acute angle, chances of endotracheal tube to be positioned on rt side are more. 2.Foreign body aspiration: The right main stem bronchus is wider shorter and vertically placed and therefore the posterior segment of rt. Upper lobe is anatomicall most susceptible to aspiration pneumonia. *Segments involved aspiration in supine position: >Rt. Upper lobe-post.segment(mostly) >Rt. lower lobe – superior segment >Lt. lower lobe – superior segment * Segments involved aspiration in sitting or errect position: >Basilar segments of rt. Lower lobe >Basilar segments of lt. lower lobe
- 44. 44 Main=primary bronchi divide into secondary=lobar bronchi, each supplies one lobe 3 on the right 2 on the left Lobar bronchi branch into tertiary = segmental bronchi Segmental bronchi further divide and redivide till terminal bronchiole. Tubes smaller than 1 mm called bronchioles Smallest, terminal bronchioles, are less the 0.5 mm diameter Terminal bronchioles loose their cartilage to form respiratory bronchiole. Lining-pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium up to terminal bronchioles after which non ciliated epithelium. Terminal bronchiole lined by nonciliated columnar epithelium Respiratory bronchiole lined by cuboidal cells Alveoli are lined by squamous cells.
- 46. Broncho pulmonary segments: *Broncho pulmonary segments are independent respiratory units. *Each segment has its own separate artery and each segment has more than one vein. *Bronchopulmonary segment is not a bronchovascular segment because it dose not have its own vein. APPLIED ANATOMY: Usually the infection of segment remains restricted to it,although some inections like TB may spread from one segment to another
- 47. 47 Respiratory Zone End-point of respiratory tree which take part in gas exchange Structures that contain air- exchange chambers are called alveoli Respiratory bronchioles lead into alveolar ducts. Ducts lead into terminal clusters called alveolar sacs – are microscopic chambers Each alveolar sac contains avg.17 alveoli
- 48. ALVEOLI *About 300 million alveoli provide an enormous membrane(50-100m2) for gas exchange in an avg.adult. *Alveolar size depends on both gravity and lung volume. *The avg. diameter 0.05-0.33mm. *In upright position largest alveoli are at the pul.apex and smallest at base. *Each alveolus is in close contact with a network of pulmonary capillaries. *The walls of alveolus are asymmetrically arranged. *On the thin side(0.4micro.m) where gas exchange occurs,the alveolar epithelium and capillary endothelium are separated by their respective cellular and basement membranes. *On the thick side(1-2micro.m), where fluid and solute exchange occurs through the pulmonary interstitial space. *The alveolar epithelium contains two types of cells: 1.Type 1 pneumocytes:Form tight junctions with one another which prevent the passage of oncotically active molecules such as albumin in to alveolus.
- 50. 2.Type 2 pneumocytes: > Produce surfactant which prevents the alveoli from collapsing by reducing surface tension. > Unlike type1 cells,these cells are capable of cell division and can produce type 1 cells if the later are destroyed. > They are also resistant to oxygen toxicity. CLINICAL IMPORTANCE: In absence of surfactant as in premature babies devlop respiratory distress syndrome.
- 51. Artery supply of bronchial tree: > Upto terminal bronchioles – bronchial artery >Beyond the terminal bronchioles-pulmonary artery Nerve supply of bronchial tree: >Parasympathetic by vagus(bronchoconstriction) >Sympathetic(T2-T5) (bronchodilatation)
- 52. MUSCLES OF RESPIRATION: *During quite inspiration: *During forced inspiration: >Diaphragm(main) >Sternocleidomastoid >External intercostal >Seratous anterior >Inter chondral portion of >Scaleni the internal intercostals >Erector spinae >Alaque nasi >Pectoralis major and minor
- 53. *During quite expiration: *During forced expiration: >Elastic recoil of alveoli and >Abdominal muscles thoracic wall >Latissimus dorsi >Internal intercostal >Transverse thoracic APPLIED ANATOMY: During anaesthesia with inhalational agents, expiration is active,mediated by abdominal muscles.
- 54. LUNGS AND PLEURA
- 55. PLEURA *Two types of pleura found in lung :Visceral pleura Parietal pleura *Visceral pleura: >It covers the surfaces and fissures of lung except at hilum. >Along the attachment of pulmonary ligament it is continuous with parietal pleura. >It is firmly adherent to lung and cannot be separated from it. >It is pain insensitive. *Parietal pleura: >It is thicker than visceral pleura. >Subdivided in to four parts: 1.Costal 2.Diaphragmatic 3.Mediastinal 4.Cervical
- 56. >There are two folds or recess of parietal pleura which act as reserve spaces for the lung to expand during deep inspiration,ie.costomediastinal recess and costodiaphragmatic recess. >Parietal pleura is pain sensitive. *In between two pleura pleural cavity present, which contains abt. 30-50 ml of fluid normally. *Nerve supply: Parietal pleura-Somatic nerve(intercostal and phrenic nerve) Visceral pleura-Autonomic nerves *blood supply: >Parietal pleura- Art.supply : Intercostal,internal thoracic, musculophrenic arteries Vein drainage: Azygos,internal thoracic vein >Visceral pleura- Art.supply: Bronchial arteries Vein drainage: Bronchial veins
- 57. LUNGS *Right lung weighs about 700 gm. *It is about 50-100 gm heavier than the left lung. *The rt lung is divided in to three lobes(upper,middle,lower) by two fissures, ie.oblique or major and horizontal or minor fissure *Left lung divided in to two lobes by oblique fissure *Surface marking: >Upper border of lung-limited up to 6cm above sternoclavicular joint. >Lower border of lung-lies on 6th rib,8th rib,10th rib on the midclavicular,midaxillary,post.scapular line respectedly. >Oblique fissure-starts from T2 posteriorly and extends obliquely downwards and forwards to the 6th costochondral junction anteriorly. >Horizontal fissure-starts from the rt 4th costochondral junction and passes horizontaly to meet oblique fissure in the mid axillary line.
- 59. Root of lung: >It connects the medial surface of the lung to the mediastinum. >Roots of the lungs lies opposite the bodies of T5-T7. >Contents: 1.Principal bronchus on the left side and eparterial,hyparterial bronchi on the right side 2.One pulmonary artery 3.Two pulmonary veins 4.Bronchial arteries, one on the rt side and two on left side 5.Bronchial vein 6.Lymphatics of lung 7.Broncho pulmonary lymh nodes 8.Areolar tissue
- 60. Differences between right and left lung Right lung Left lung 1.It has 2 fissures and 3 lobes. 1.It has one fissure and 2 lobes. 2.Anterior border is straight. 2.Ant.border is interrupted by the cardiac notch. 3.Larger and heavier 3.Smaller and lighter 4.Shorter and broader 4.Longer and narrower
- 61. COMPARISION BETWEEN PEDIATRIC & ADULT AIRWAY 1– Relatively larger tongue – Obligate nasal breather. 2 – Large & omega-shaped epiglottis 3 –In children the angle of both rt. And lt.bronchus is same,ie;55 degree upto the age of 3 yrs. 4 - Narrowest part of pediatric airway is cricoids cartilage or subglottis up to the age of 5 yrs.. 5 – Angled vocal cord – Infant VC have more angled attachment to thyroid angle whereas adult VC are more perpendicular.
- 63. PLEURAL EFFUSION
- 64. EMPHYSEMA
- 65. PNEUMOTHORAX
- 68. BRONCHIECTASIS
- 69. REFERENCES: Benumof’s Airway Management (3rd edition) Miller’s Anesthesia (7th edition) Morgan Clinical Anesthesiology (5th edition ) Rashid M Khan airway management(4th edition) Ajay Yadav text book of anaesthesia(4th edition) B D Chaurasia human anatomy Grays anatomy E-books
- 70. THANK YOU