Blockchain Network Theory
•Télécharger en tant que PPTX, PDF•
4 j'aime•2,752 vues
Blockchain distributed ledger technology is evolving from the hype phase into one of greater maturity and long-term value creation. This graduate course overview examines how blockchains, networks, and social interaction patterns are related.
Signaler
Partager
Signaler
Partager
Recommandé
Recommandé
Contenu connexe
Tendances
Tendances (20)
Ethereum Tutorial - Ethereum Explained | What is Ethereum? | Ethereum Explain...

Ethereum Tutorial - Ethereum Explained | What is Ethereum? | Ethereum Explain...
Blockchain Technology | Blockchain Explained | Blockchain Tutorial | Blockcha...

Blockchain Technology | Blockchain Explained | Blockchain Tutorial | Blockcha...
Similaire à Blockchain Network Theory
ABSTRACT
Blockchain technology is often referred to as a groundbreaking innovation and the harbinger of a new economic era. Blockchains may be capable of engendering a new type of economic system: the blockchain economy. In the blockchain economy, agreed-upon transactions would be enforced autonomously, following rules defined by smart contracts. The blockchain economy would manifest itself in a new form of organizational design—decentralized autonomous organizations (DAO)—which are organizations with governance rules specified in the blockchain. We discuss the blockchain economy along dimensions defined in the IT governance literature: decision rights, accountability, and incentives. Our case study of a DAO illustrates that governance in the blockchain economy may depart radically from established notions of governance. Using the three governance dimensions, we propose a novel IT governance framework and a research agenda for governance in the blockchain economy. We challenge common assumptions in the blockchain discourse, and propose promising information systems research related to these assumptions.Governance in the Blockchain Economy: A Framework and Research Agenda. Roman...

Governance in the Blockchain Economy: A Framework and Research Agenda. Roman...eraser Juan José Calderón
Blockchain Technology and Decentralized Governance: Is the State Still Necessary?
Marcella Atzori, Ph. D.*
ABSTRACT
The core technology of Bitcoin, the blockchain, has recently emerged as a disruptive innovation with a wide range of applications, potentially able to redesign our interactions in business, politics and society at large. Although scholarly interest in this subject is growing, a comprehensive analysis of blockchain applications from a political perspective is severely lacking to date. This paper aims to fill this gap and it discusses the key points of blockchain-based decentralized governance, which challenges to varying degrees the traditional mechanisms of State authority, citizenship and democracy. In particular, the paper verifies to which extent blockchain and decentralized platforms can be considered as hyper-political tools, capable to manage social interactions on large scale and dismiss traditional central authorities. The analysis highlights risks related to a dominant position of private powers in distributed ecosystems, which may lead to a general disempowerment of citizens and to the emergence of a stateless global society. While technological utopians urge the demise of any centralized institution, this paper advocates the role of the State as a necessary central point of coordination in society, showing that decentralization through algorithm-based consensus is an organizational theory, not a stand-alone political theory.
Keywords: Bitcoin, blockchain, Decentralized Autonomous Organizations, decentralization, democracy, Ethereum, encryption, governance, politics, State, peer-to-peer networksBlockchain Technology and Decentralized Governance: Is the State Still Necess...

Blockchain Technology and Decentralized Governance: Is the State Still Necess...eraser Juan José Calderón
Similaire à Blockchain Network Theory (20)
State of Blockchain 2017: Smartnetworks and the Blockchain Economy

State of Blockchain 2017: Smartnetworks and the Blockchain Economy
BlockChain for the Humanitarian Sector - Future Opportunities - November 2016

BlockChain for the Humanitarian Sector - Future Opportunities - November 2016
Block chain for the humanitarian sector - future opportunities

Block chain for the humanitarian sector - future opportunities
Governance in the Blockchain Economy: A Framework and Research Agenda. Roman...

Governance in the Blockchain Economy: A Framework and Research Agenda. Roman...
From Bitcoin to Blockchain: Industry Review April 2017 from OLMA NEXT Ltd

From Bitcoin to Blockchain: Industry Review April 2017 from OLMA NEXT Ltd
Blockchain Technology and Decentralized Governance: Is the State Still Necess...

Blockchain Technology and Decentralized Governance: Is the State Still Necess...
Blockchain Technology: A Sustainability Perspective

Blockchain Technology: A Sustainability Perspective
Blockchain-Based Internet of Things: Review, Current Trends, Applications, an...

Blockchain-Based Internet of Things: Review, Current Trends, Applications, an...
Blockchain-Based Internet of Things: Review, Current Trends, Applications, an...

Blockchain-Based Internet of Things: Review, Current Trends, Applications, an...
Plus de Melanie Swan
Plus de Melanie Swan (20)
AI Health Agents: Longevity as a Service in the Web3 GenAI Quantum Revolution

AI Health Agents: Longevity as a Service in the Web3 GenAI Quantum Revolution
Quantum Intelligence: Responsible Human-AI Entities

Quantum Intelligence: Responsible Human-AI Entities
The Human-AI Odyssey: Homerian Aspirations towards Non-labor Identity

The Human-AI Odyssey: Homerian Aspirations towards Non-labor Identity
Quantum Information Science and Quantum Neuroscience.ppt

Quantum Information Science and Quantum Neuroscience.ppt
Quantum Neuroscience: CRISPR for Alzheimer’s, Connectomes & Quantum BCIs

Quantum Neuroscience: CRISPR for Alzheimer’s, Connectomes & Quantum BCIs
Art Theory: Two Cultures Synthesis of Art and Science

Art Theory: Two Cultures Synthesis of Art and Science
Dernier
Dernier (20)
Cloud Frontiers: A Deep Dive into Serverless Spatial Data and FME

Cloud Frontiers: A Deep Dive into Serverless Spatial Data and FME
Mastering MySQL Database Architecture: Deep Dive into MySQL Shell and MySQL R...

Mastering MySQL Database Architecture: Deep Dive into MySQL Shell and MySQL R...
Tata AIG General Insurance Company - Insurer Innovation Award 2024

Tata AIG General Insurance Company - Insurer Innovation Award 2024
Scaling API-first – The story of a global engineering organization

Scaling API-first – The story of a global engineering organization
TrustArc Webinar - Stay Ahead of US State Data Privacy Law Developments

TrustArc Webinar - Stay Ahead of US State Data Privacy Law Developments
AWS Community Day CPH - Three problems of Terraform

AWS Community Day CPH - Three problems of Terraform
Top 10 Most Downloaded Games on Play Store in 2024

Top 10 Most Downloaded Games on Play Store in 2024
The 7 Things I Know About Cyber Security After 25 Years | April 2024

The 7 Things I Know About Cyber Security After 25 Years | April 2024
Strategies for Landing an Oracle DBA Job as a Fresher

Strategies for Landing an Oracle DBA Job as a Fresher
Apidays New York 2024 - The Good, the Bad and the Governed by David O'Neill, ...

Apidays New York 2024 - The Good, the Bad and the Governed by David O'Neill, ...
Boost PC performance: How more available memory can improve productivity

Boost PC performance: How more available memory can improve productivity
Boost Fertility New Invention Ups Success Rates.pdf

Boost Fertility New Invention Ups Success Rates.pdf
Connector Corner: Accelerate revenue generation using UiPath API-centric busi...

Connector Corner: Accelerate revenue generation using UiPath API-centric busi...
Top 5 Benefits OF Using Muvi Live Paywall For Live Streams

Top 5 Benefits OF Using Muvi Live Paywall For Live Streams
Blockchain Network Theory
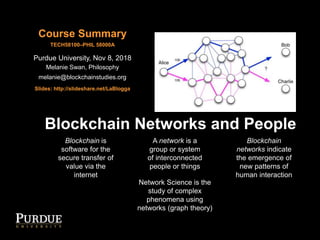
- 1. Blockchain Networks and People Blockchain is software for the secure transfer of value via the internet A network is a group or system of interconnected people or things Network Science is the study of complex phenomena using networks (graph theory) Blockchain networks indicate the emergence of new patterns of human interaction Purdue University, Nov 8, 2018 Course Summary Slides: http://slideshare.net/LaBlogga Melanie Swan, Philosophy melanie@blockchainstudies.org TECH58100–PHIL 58000A
- 2. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Agenda Readings Summary Blockchain Overview Network Overview 1
- 3. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Readings #1: Bitcoin & Network Science 2 Nakamoto, S. (2008). Bitcoin: P2P Electronic Cash Original white paper for blockchain concept: having an always-on Internet-based system checking in real-time 24-7 anytime anyone tries to spend digital cash, to control that it is only being spent once (solution to double-spending problem) Brandes et al. (2013). What is network science? A network connects nodes, resource flow is not necessary (example: Purdue alumni network) A network is a model of a real-life phenomenon Core-periphery: densely-connected core, sparsely- connected periphery Ego Network: focal node (“ego”) and directly-connected nodes ( “alters”)
- 4. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Readings #2: Blockchain & Network Intro 3 Morabito. (2017). Blockchain for Business Innovation Decentralized database: all peer nodes have a copy Public blockchains vs. private blockchains (for business) Proof of work and proof of stake consensus algorithms Smart contracts: two or more parties, terms, consideration Jackson. (2008). Social and Economic Networks Intro General measures of network utility, efficiency, stability Trade-offs in network design: stability vs. efficiency Homophily: tendency of individuals to associate and bond with others that are similar, “birds of a feather flock together” Preferential attachment: “rich get richer”
- 5. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Readings #3: Water Industry & Scale-free 4 Lin et al. (2017). Blockchain and ICT E-Agriculture IOT and blockchain networks (Bitcoin, Ripple, Monero) indicate complex network behavior: small-world & scale-free Interpretation: replicating the “regular” way of doing things Sohn. (2017). Small-World and Scale-Free Network Models for IoT Systems Random networks (Erdős–Rényi, PMI, 1959): Normally-distributed; Gaussian Small-world networks (Watts & Strogatz, Nature, 1998): Power law; 80-20 pareto distribution Scale-free networks (Barabási & Albert, Science, 1999): Fat-tailed distribution; six degrees of separation; rich get richer
- 6. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Readings #4: Agriculture & Network Trust 5 Kim and Laskowski. (2017). Agriculture & Blockchain: Sustainable Solutions for Food, Farmers, & Financing Blockchain enables new models of local organizing: farmers cooperatives, recourse against players with market power Food safety, product traceability (salmonella outbreak) Sustainability: financial, crop genetics, micro-insurance Sherchan et al. (2013). Trust in Social Networks. Humanity is good at producing material goods (“widgets”), how can we also excel at producing intangible resources? Social capital (trust, autonomy, inclusion, recognition, peace) Incentive structures that promote social capital production
- 7. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Readings #5: Solar Energy & Network Stack 6 Adjeleian et al. (2018). How blockchain is disrupting the Solar Energy industry Incentives for transitioning to renewable resources IOT carbon sequestration blockchain for carbon credits Implied political power shift due to energy independence Orlikowski and Scott. (2015). The algorithm and the crowd: considering the materiality of service innovation Digital services: shift to practice of buying airline tickets online Building the trust stack: design structures to create social capital in a digital network environment Layers in the trust stack: infrastructure, interface, application, network resources (trust, liquidity)
- 8. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Agenda Readings Summary Blockchain Overview Network Overview 7
- 9. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks 8 “Better horse” Progression of a New Technology “Horseless carriage” “Car” 3.0 2.0 1.0 Better internet: payments and secure information transfer, privacy-protected computing Assets digitized and registered to blockchains, real-time valuation and transfer, smart contracts Large-scale social collaboration technology: supplementing and replacing governments, corporations, and open-source communities Source: Swan, M. (2015). Blockchain: Blueprint for a New Economy Blockchain
- 10. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks basics. 9
- 11. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks internet content. 10 information. email. voice. video. money.
- 12. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks 11 Conceptual Definition: Blockchain is a software protocol; just as SMTP is a protocol for sending email, blockchain is a protocol for sending money Source: http://www.amazon.com/Bitcoin-Blueprint-New-World-Currency/dp/1491920491 What is Blockchain/Distributed Ledger Tech?
- 13. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Blockchain Technology: What is it? 12 Blockchain technology is the secure distributed ledger software that underlies cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin “Internet of Money” leapfrog technology; Skype is an app allowing phone calls via Internet without POTS; Bitcoin is an app allowing money transfer via Internet without banks; ‘decentralized Paypal’ Internet (decentralized network) Blockchain Bitcoin Source: http://www.amazon.com/Bitcoin-Blueprint-New-World-Currency/dp/1491920491 Application Layer Protocol Layer Infrastructure Layer SMTP Email VoIP Phone calls OSI Protocol Stack:
- 14. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Chain of linked blocks = a “blockchain” 13 Source: GREG/Smart Energy Meeting PWC, Blockchain101, Nov 2016 Each block stores information and contains a validated pointer (called a hash) to the previous block. Each block is thus linked or “chained” to the last one The chaining of blocks is tamper-proof, creating a immutable record of events that is resistant to fraud and corruption
- 15. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks blockchain. 14 software. secure cryptographic transfer. internet.
- 16. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks killer apps. 15 secure transfer of value, of… money & securities. property. contracts. identity credentials.
- 17. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks How does Bitcoin work? Use eWallet app to submit transaction 16 Source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t5JGQXCTe3c Scan recipient’s address and submit transaction $ appears in recipient’s eWallet Wallet has keys not money Creates PKI Signature address pairs A new PKI signature for each transaction
- 18. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks P2P network confirms & records transaction 17 Source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t5JGQXCTe3c Transaction computationally confirmed Ledger account balances updated Peer nodes maintain distributed ledger Transactions submitted to a pool and miners assemble new batch (block) of transactions each 10 min Each block includes a cryptographic hash of the last block, chaining the blocks, hence “Blockchain”
- 19. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks 18 public chains. private chains. trustless. mined. p2p software. trusted. not-mined. enterprise software.
- 20. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks What is blockchain? Conceptual overview 1. Digital money (better version of PayPal/Venmo) 2. Enterprise software (digital asset inventories) 3. Inclusion technology (unbanked, credit, literacy) 4. Emerging legal jurisdiction (game theory not police) 5. Web 3.0: large-scale collaboration technology (Web 3.0 = smart network, “Internet's new pipes”) 6. Truth verification method (rich information attributes) 19 Smart networks: intelligent autonomously-operating networks, a new form of global computational infrastructure that includes technologies such as blockchain economic networks, deep learning pattern- recognition networks, autonomous-strike UAVs, and high- frequency trading networks
- 21. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Agenda Readings Summary Blockchain Overview Network Overview 20
- 22. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Complex Systems 21 Can often characterize the macrostate and the microstate, but what happens in the middle? Macrostate: GDP Microstate: Rate of new businesses formation, new auto loans Middle: Complexity Source: Schweitzer, F., et al. 2009. Economic Networks: The New Challenges. Science. 325:422-5. Simon, H.A. 1996. The Sciences of the Artificial. Third edition. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. Simon (1996): small groups of parts make up larger assemblies (modules) from which the whole is built; the parts of the module interact strongly Whole Assemblies or Modules Parts Simon (1996)Schweitzer (2009)
- 23. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Huntington’s disease (0.0002% deaths, 2.27 per million) Heart disease (30%/22% U.S./global deaths), Cancer (24% U.S. deaths) “Natural Causes” attributed due to lack of causal model 22 Solving Disease and Health Challenges Hard problems: probabilistic not deterministic Genomics 100% Behavior 33% Genomics 33% Environment 33% Source: Pagidipati. 2013. Estimating Deaths From Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation. 127(6):749–756; National Cancer Institute. 2018. Cancer Statistics. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/understanding/statistics Deterministic Probabilistic 40+ CAG repeats in the HTT gene
- 24. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Problem: Prediction in Complex Systems How are these events similar? different? Is the Turkish coup an example in this trajectory? How can networks be used to map the underlying factors that give rise to macro-level formations? 23 1789 2010 ??? French Revolution Tiananmen Square Next event Arab Spring Turkish coup? 1989 2016 Source: Handbook of Cliometrics. 2016. Editors: Diebolt, Claude, Haupert, Michael (Eds.)
- 25. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Claim: Networks are a way to analyze “the middle” 24 Map relationships between agents to see intermediate structure, dynamic emergence
- 26. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Drawing the Graph 1. What is the domain? 2. What are the entities in this domain? (nodes) 3. What are the relationships between them? (edges) 25 Simple Graph of Entities and Relationships Domain: Social Network Domain: Financial System Nodes: People Edges: Know one another Edges: Financial obligation (1: cash deposits, 2: loans) Nodes: Banks
- 27. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Network Science Network Science = The study of graphs as a representation of relations between entities Nodes and edges (entities and relationships between them) Seven Bridges of Königsberg (Euler, 1736, graph theory) 26 node or
- 28. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Network Science Seven Bridges of Königsberg (Euler, 1736, graph theory) Problem: walk around the city, crossing each bridge only once Euler: mathematical proof that it cannot be done, using (inventing) graph theory; shifting math from ‘science of quantity’ to more abstract structures such as topology 27 node or Kant’s Tomb, Kaliningrad Cathedral (formerly Königsberg)
- 29. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Example: Social Networks 28
- 30. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Example: Food Web and Trade Network 29
- 31. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Example: Systemic Financial Risk Risk of financial contagion (how “catching” the collapse of one bank would be to others given linked exposure) 30 Source: IMF, June 2016, Systemic Risk Among Deutsche Bank and Global Systemically Important Banks Legend: • Blue, purple and green nodes correspond to European, US and Asian banks • Arrow thickness captures total linkages (both inward and outward), • Arrow direction is net spillover • Node size corresponds to asset value
- 32. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Example: How are brain and body linked? 31 Sources: Murphy, Bassett, et al. 2018. Structure, function, and control of the human musculoskeletal network. PLOS Biology. Davies, J.A. 2014. Life Unfolding: How the Human Body Creates Itself. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Summary: Employ network theory methods to map neural control mechanisms to the musculoskeletal system Summary: study biological networks: larger patterns of gene expression and cellular interconnection Biological musculoskeletal network
- 33. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Drawing the Graph Different ways to organize information 32 Traditional Method Network Science Method
- 34. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Network Properties Use networks to analyze innovation rate, collaboration with other departments/firms, how decisions are made 33 Degree of connectivity of network • V:={1,2,3,4,5,6} • E:={{1,2},{1,5},{2,3},{2,5},{3,4},{4,5},{4,6}} How quickly is a new idea disseminated? Who is a key influencer in decisions?
- 35. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Build a Social Graph – How does it work? Compile table listing names and number of interactions 34 • V:={1,2,3,4,5,6} • E:={{1,2},{1,5},{2,3},{2,5},{3,4},{4,5},{4,6}} Source: https://www.teachengineering.org/activities/view/uno_graphtheory_lesson01_activity1 Data Network Modeling
- 36. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Build a Social Graph – How does it work? Example: Medea (Euripides), 431 BC Level 1 analysis: purely quantitative, based on # interactions 35 • V:={1,2,3,4,5,6} • E:={{1,2},{1,5},{2,3},{2,5},{3,4},{4,5},{4,6}} Source: https://www.teachengineering.org/activities/view/uno_graphtheory_lesson01_activity1 Basic Interaction Map Network Modeling Network Analysis Medea Jason
- 37. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Build a Social Graph Example: tweet activity during conference 36 • V:={1,2,3,4,5,6} • E:={{1,2},{1,5},{2,3},{2,5},{3,4},{4,5},{4,6}} Source: https://pegasusdata.com/2012/12/06/just-in-time-sociology-new-field-digital-humanities/ Conference Agenda
- 38. 8 Nov 2018 Blockchain Networks Build a Social Graph Example: tweet activity during conference 37 • V:={1,2,3,4,5,6} • E:={{1,2},{1,5},{2,3},{2,5},{3,4},{4,5},{4,6}} Source: https://pegasusdata.com/2012/12/06/just-in-time-sociology-new-field-digital-humanities/ Keynote: Paula Tubaro Conference Organizer: Frederic Kaplan
